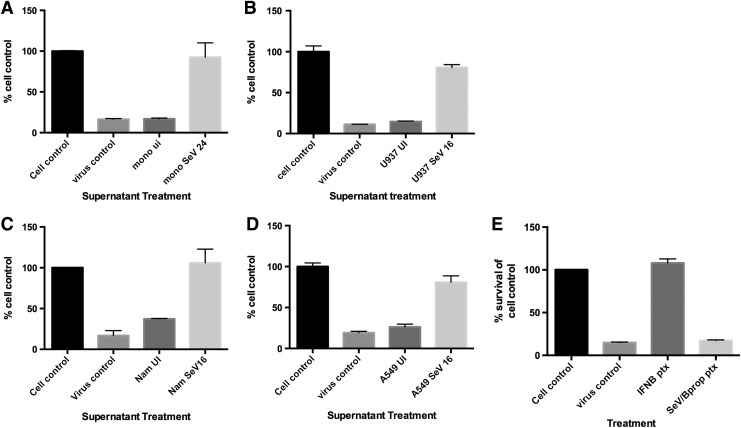
FIG. 1.
Multiple cell types produce biologically active type I IFNs upon SeV infection. (A) Supernatants from primary monocytes that were either UI or infected with SeV (150 HA U/mL) for 24 h were treated with β-propiolactone to inactivate the virus and then used to pretreat fresh U937 cells for 24 h. The U937 cells were then infected with VSV for 72 h and cell viability was measured via MTT assay. Cell viability is shown as the % of cell control. Cell control: UI, untreated. Virus control: VSV infected, untreated. Supernatants from UI or SeV infected (B) U937, (C) Namalwa, or (D) A549 cells for 16 h were treated with β-propiolactone to inactive the virus and then used to pretreat fresh U937 cells for 24 h. The U937 cells were then infected with EMCV for 72 h and cell viability was measured via MTT assay. Cell viability is shown as the % of cell control. Cell control: UI, untreated. Virus control: EMCV infected, untreated. Data shown are from 3 independent biological replicates. (E) U937 cells were pretreated with IFN-β (100 U/mL) or supernatants from U937 cells treated with β-propiolactone-inactivated SeV (150 HA U/mL) for 24 h. The U937 cells were then infected with EMCV for 72 h and cell viability was measured via MTT assay. Cell control: UI, untreated. Virus control: EMCV infected, untreated, IFNB ptx: pretreated with IFN-β; SeV/Bprop ptxt: treated with inactivated SeV by β-propiolactone. SeV, Sendai virus; IFN, interferon; UI, uninfected; HA, hemagglutination; VSV, vesicular stomatitis virus; EMCV, encephalomyocarditis virus.