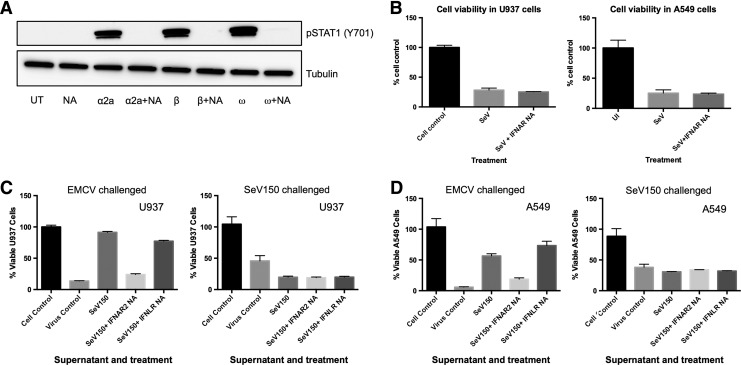
FIG. 5.
Inhibiting canonical type I IFN signaling during SeV infection does not affect SeV-mediated CPE. (A) U937 cells were treated with 1000 U/mL of IFN-α2a, IFN-β, or IFN-ω for 1 h in the presence or absence of the IFNAR2 neutralizing antibody. Western blot analysis was performed to detect phosphorylated STAT1(Y701) and tubulin was used as the loading control. UT: untreated; NA: cells treated with IFNAR2 neutralizing antibody alone; α2a: IFN-α2a treated; α2a + NA: cells treated with both antibody and IFN-α2a; β: IFN-β treated; β + NA: cells treated with both antibody and IFN-β; ω: IFN-ω treated; and ω + NA: cells treated with both antibody and IFN-ω. (B) U937 (panel 1) and A549 cells (panel 2) were infected with SeV (150 HA U/mL) in the presence or absence of IFNAR2 neutralizing antibody. Cell viability was measured 72 h pi. Data are representative of 3 independent biological replicates. Supernatants from cells infected with SeV (150 HA U/mL) for 16 h were inactivated (β-propiolactone) and used to pretreat fresh (C) U937 and (D) A549 cells for 24 h in the presence or absence of the IFNAR or IFNLR neutralizing antibodies. The U937 cells were then infected with either EMCV or SeV (150 HA U/mL) for 72 h and cell viability was measured via MTT assay (U937) or crystal violet assay (A549). Results are shown as the % of cell control. SeV150: virus-inactivated supernatant from SeV-infected cells (150 HA U/mL); SeV150 + IFNAR2 NA: treated with virus-inactivated supernatant from SeV-infected cells (150 HA U/mL) in the presence of IFNAR2-neutralizing antibody; SeV150 + IFNLR NA: treated with virus-inactivated supernatant from SeV-infected cells (150 HA U/mL) in the presence of IFNLR-neutralizing antibody. IFNAR, IFN receptor; IFNLR, IFN-lambda receptor.