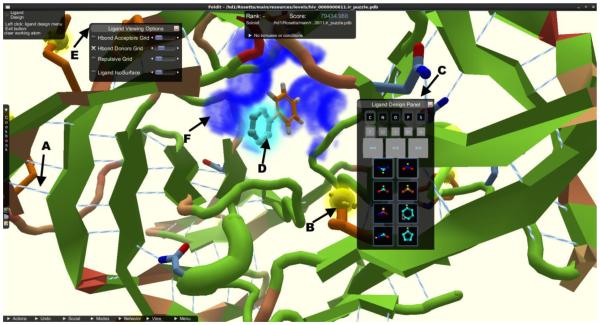
Fig. 13.
Screenshot of Foldit, from the new Rosetta Ligand application, a crowd-sourced multiplayer game adopted for ligand design. A) Hydrogen bond contacts are shown in light-blue/white lines and B) surface exposed hydrophobic residues are shown as yellow blobs. C) The ligand design panel is the control center for players and allows them to choose from a variety of fragments, bond manipulations, and element modifications to design the ligand in the protein binding pocket. D) When players hover over a fragment, a ghost view of the new fragment is drawn at the attachment point (light blue glowing fragment). E) The ligand viewing options menu allows players to turn off QSAR grids calculated for hydrogen bond acceptors and donors F) (shown as dark blue fog) or repulsion for the ligand, with slider bars on the side to adjust the alpha of the drawn fogs. Players can turn on the protein isosurface or a ligand centric view that draws the isosurface around the ligand, allowing for advance spatial alignment of the ligand in the binding pocket.