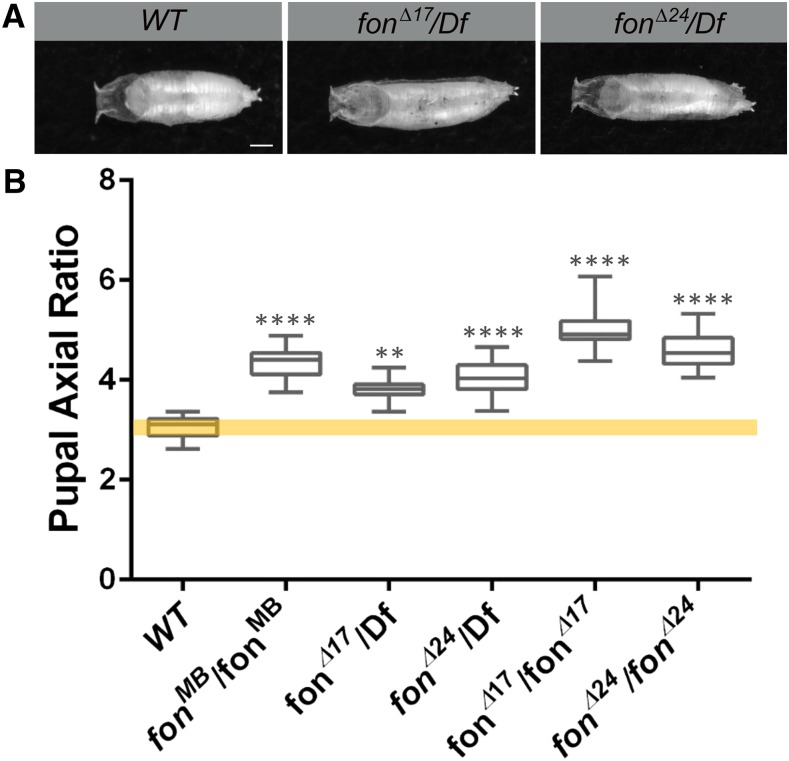
Figure 1.
Mutations in fon result in elongated pupal phenotypes. (A) Pupal cases of control (WT) or fon mutations (fonΔ17 and fonΔ24) analyzed over a deficiency chromosome (Df) that removes the fon locus. (B) Measurement and quantitation of axial ratios (length/width) of the indicated pupal genotypes demonstrate that fon mutants are defective in the ability to shorten their pupal case (17 ≤ n ≤ 35 for each genotype). Mean ± SD; P-values: ** P < 0.01, **** P < 0.001. Bars, 0.75μm.