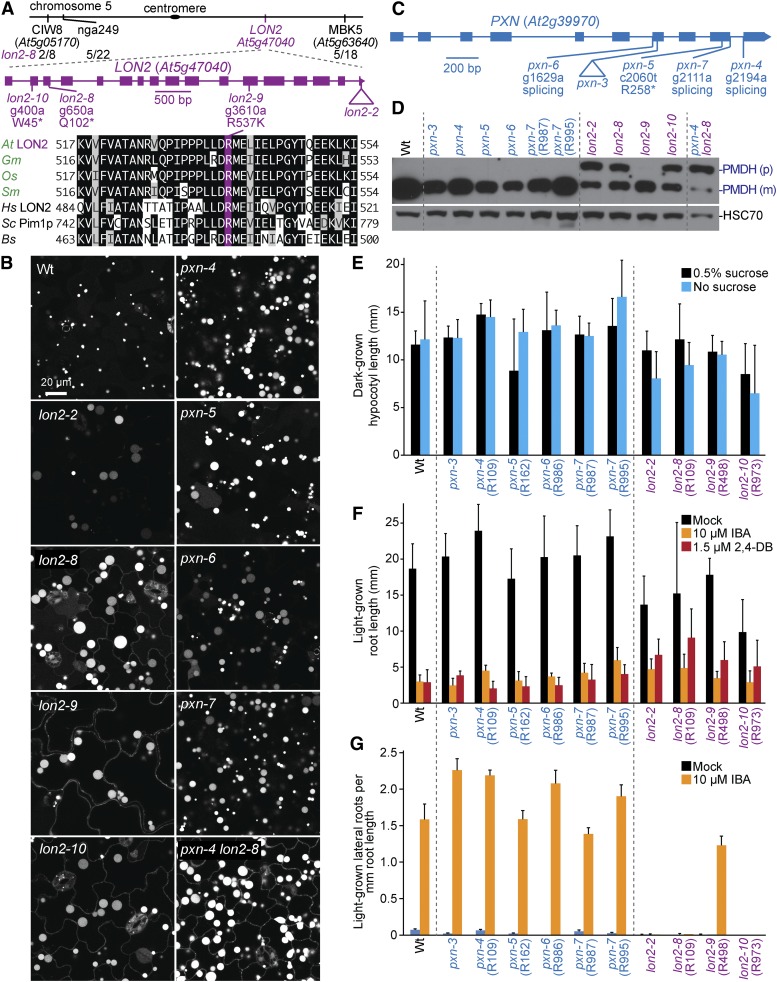
Figure 12.
Mutations in LON2 and PXN lead to enlarged GFP-PTS1 puncta, and a subset of lon2 mutants display GFP-PTS1 mislocalization to the cytosol, PTS2-processing defects, and IBA resistance in lateral root production. (A) Chromosome map indicates the positions of markers used to map lon2-8 and ratio of recombinants to the number of chromosomes assessed. A gene diagram indicates the positions of lon2 mutations. LON2 was aligned with related proteins (Table S4); residues are shaded when identical (black or purple) or chemically similar (gray) in at least four sequences. (B) Confocal micrographs were taken of cotyledon epidermal cells of 8-day-old seedlings expressing peroxisomally targeted fluorescence (GFP-PTS1; white). (C) A gene diagram indicates the positions of pxn mutations. (D) Eight-day-old seedlings were prepared for immunoblot analysis and serially probed with antibodies recognizing the indicated proteins. PMDH is translated as a precursor (p) with a PTS2 that is cleaved in the peroxisome to yield mature (m) protein. HSC70 was used as a loading control. (E) Hypocotyl lengths of 5-day-old dark-grown seedlings were measured. Error bars show SD (n ≥ 15). (F) Root lengths of 8-day-old light-grown seedlings were measured. Error bars show SD (n ≥ 17). (G) Seedlings were grown in the absence of hormone for 4 days and then transferred to either media without hormone or supplemented with IBA for an additional 4 days. The number of lateral roots and root lengths were measured, and the ratio is shown. Error bars show SD (n = 20). Data are representative of two (B, D, E, and G) or three (F) replicates. Bar, 20 µm.