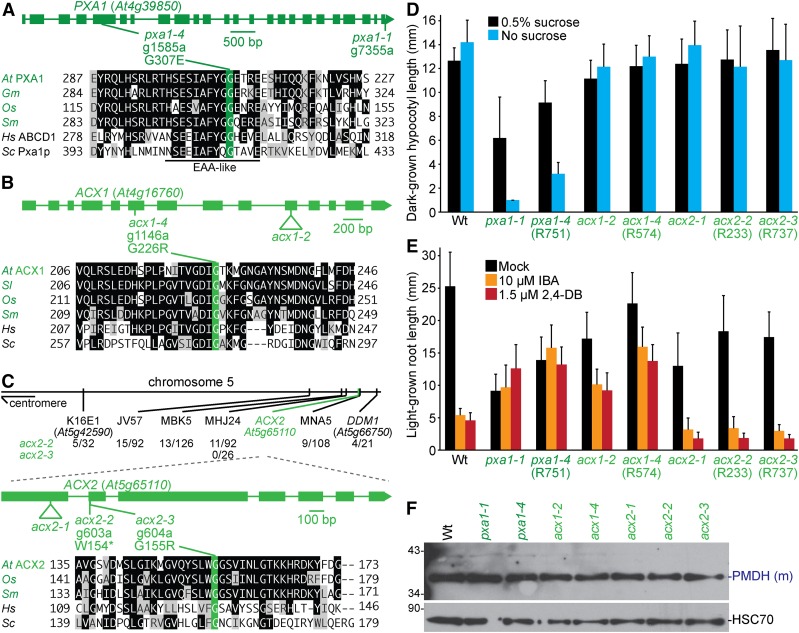
Figure 6.
Mutations in PXA1 confer sucrose dependence and IBA and 2,4-DB resistance, and mutations in ACX1 lead to IBA and 2,4-DB resistance, whereas mutations in ACX2 do not generate notable physiological defects. (A–C) Gene diagrams indicate positions and nature of pxa1 (A), acx1 (B), and acx2 (C) mutations. PXA1 (A), ACX1 (B), and ACX2 (C) were aligned with related proteins (Table S4); residues are shaded when identical (black or green) or chemically similar (gray) in at least four (A, B) or three (C) sequences. Chromosome map indicates the positions of markers used to map acx2 mutants and ratios of recombinants to the number of chromosomes assessed (C). (D) Hypocotyl lengths of 5-day-old dark-grown seedlings were measured. Error bars show SD (n = 20). (E) Root lengths of 8-day-old light-grown seedlings were measured. Error bars show SD (n ≥ 14). Data are representative of two (D) or three (E) replicates. (F) Eight-day-old seedlings were prepared for immunoblot analysis and serially probed with antibodies recognizing the indicated proteins. PMDH is translated as a precursor with a PTS2 that is cleaved in the peroxisome to yield mature (m) protein. HSC70 was used as a loading control. Positions of molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left.