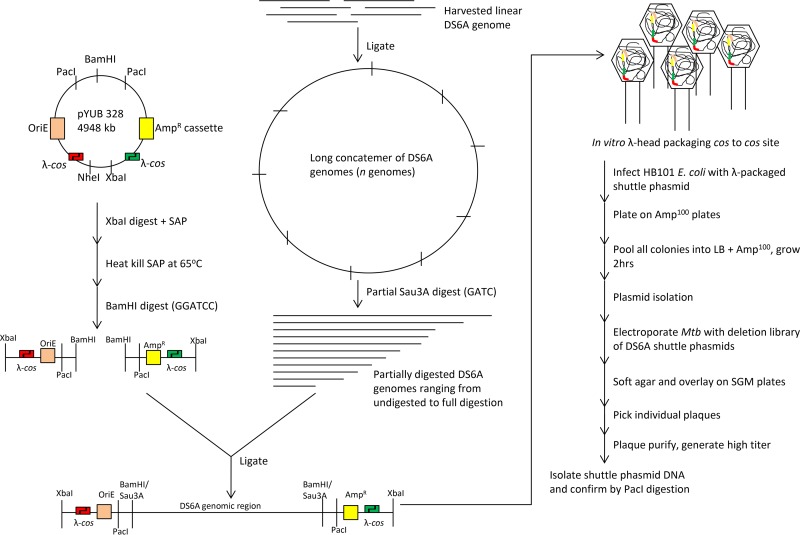
FIG 1.
Schematic of the multistep construction of a DS6A shuttle phasmid. DS6A genomic DNA isolated from phage is linear and was ligated to concatemerize. Partial Sau3AI digestion was used to delete random regions of 1 to 10 kb. The cohesive ends generated by Sau3AI are compatible with the two BamHI fragments generated from pYUB328, and the ligation of the two pYUB328 fragments to Sau3AI-digested DS6A resulted in a linear DNA fragment flanked by λ-cos sites at each end. Incubation of this ligation mix with in vitro λ-packaging mix started the packaging reaction by cutting at the first cos site, followed by inserting the DNA from the first cos site to the second cos site, and terminating the packaging reaction by cutting the second cos site. Transduction of in vitro packaged λ to E. coli HB101 delivered the linear DNA from λ heads to E. coli. The two cohesive ends of the λ-cos site were ligated to circularize. This process generated a phasmid library where modified pYUB328 DNA (with one cos site) is inserted at random places in the DS6A genome. Transformation of this library into M. tuberculosis generates DS6A plaques in cases where the recombinant DNA has replaced a small nonessential region of DS6A DNA. The deletion sites in these phages were determined by sequencing. AmpR, ampicillin resistance; Amp100, 100 µg/ml ampicillin; Mtb, M. tuberculosis.