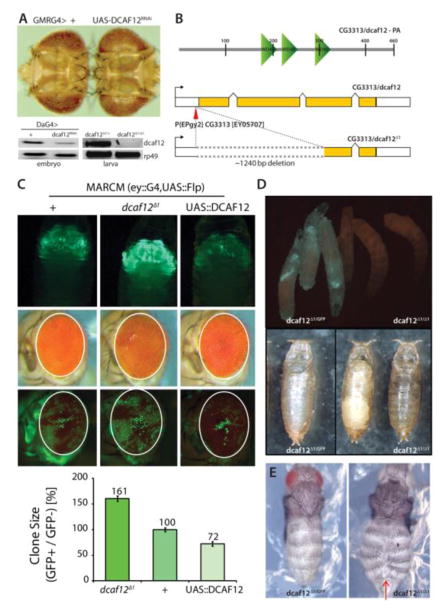
Figure 1. Effects of DCAF12 on retinal growth.
A) Knockdown of CG3313/dcaf12 in the developing retina causes tissue overgrowth. GMRGal4 expresses UAS-linked transgenes in all cells of the developing retina posterior to the morphogenetic furrow. The CG3313RNAi transgene effectively decreases CG3313 expression (lower panel, DA-Gal4 expresses UAS-linked transgenes ubiquitously). CG3313 transcripts are also undetectable in larvae of homozygous dcaf12Δ1/Δ1 mutant animals. The endogenous transcript of dcaf12 was amplified using RT-PCR (40 cycles).
B) Schematic representations of DCAF12 protein structure (upper) and of dcaf12Δ1 generated from EPgy2 element EY05707 by imprecise excision (lower). About 1240 nucleotides were deleted from the first to third exon in dcaf12Δ1. DCAF12 contains four WD40-repeats. dcaf12 sequence is 51% similar to human WDR40a/dcaf12 (ClustalW).
C) GFP-marked clones generated throughout eye development using the MARCM system (eyelessGal4, UAS-FLP; act>y+>Gal4, UAS-GFP; FRT82B, tubGal80). Upper: Overexpression of dcaf12 limits clonal growth, while clones homozygous for dcaf12Δ1 over-grow. Representative images of each genotype are shown. Despite the difference in clones, the entire eye structure is not significantly affected. Lower: Quantification of clone sizes using Image J and Phenocapture ®.
D) Comparison of sibling 3rd instar larvae heterozygous (left, carrying a GFP-expressing balancer chromosome) or homozygous for dcaf12Δ1 (right). Eggs were collected for ~ 4 hours and the crawling third instar larvae were examined at ~ 110 hours AEL.
dcaf12Δ1/Δ1 is lethal at pupal stage. Pupae of each genotype were examined ~124 hours AEL. The left panel shows an empty pupal case of a heterozygote (dcaf12Δ1/+ ), and the right panel shows arrested homozygous pupae. Heterozygous pupae emerged as adults ~120 AEL but homozygotes never emerged even after ~15days.
E) Abdominal closure defect in dcaf12Δ1/Δ1. Pharate adults of each genotype were dissected and examined. dcaf12Δ1 homozygotes exhibit frequent clefts in the dorsal abdominal cuticle, but no obvious phenotype was observed in dcaf12Δ1 heterozygotes.