Fig. 3. Effect of a high K+-induced membrane depolarization on PAP in the control and PAH-MCT rats.
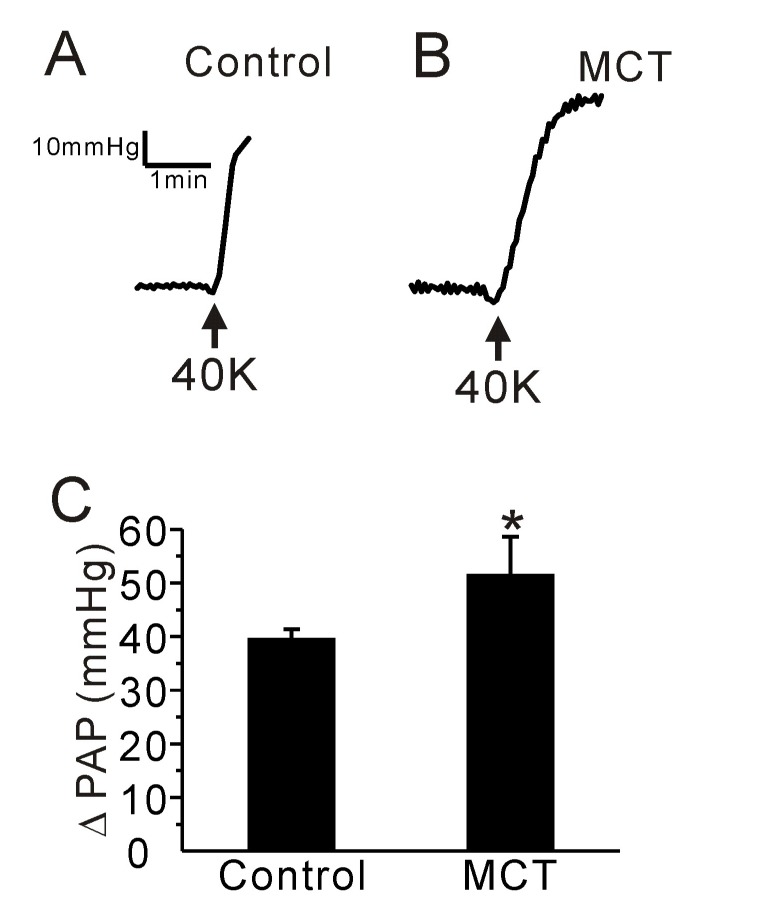
(A, B) Representative traces of PAP recording in the control (A) and PAH-MCT (B) rats. Application of a high potassium concentration (40 mM KCl, 40K) induced an increase of PAP in both groups. (C) The amplitude of PAP (ΔPAP) is shown as bar graphs. The ΔPAP in the presence of 40K was higher in the PAH-MCT group than in the control. *p<0.05.
