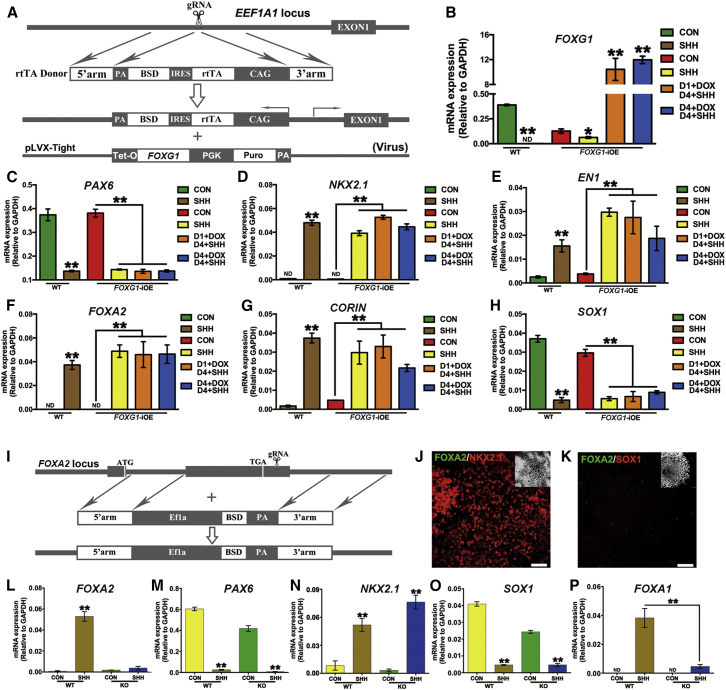
Figure 3.
Targeting FOXG1 and FOXA2 Fails to Bring the AD Cells an MGE Identity
(A) Schematic representation of the strategy in construction of FOXG1-iOE hESCs.
(B–H) mRNA levels of FOXG1, PAX6, NKX2.1, EN1, FOXA2, CORIN, and SOX1 in day-12 AD differentiated wild-type (WT) or FOXG1-iOE hESCs in the absence or presence of SHH. In some groups, doxycycline (Dox) is added to the FOXG1-iOE hESCs to induce exogenous FOXG1 expression. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Unpaired two-tailed Student's t test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
(I) Schematic representation of the strategy in construction of FOXA2 KO hESCs.
(J and K) Confocal images show NKX2.1+/SOX1− FP-like cells induced in SHH-treated FOXA2 KO cells under AD conditions. Insets show Hoechst counterstaining of nuclei. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(L–P) FOXA2, PAX6, NKX2.1, SOX1, and FOXA1 mRNA expression in day-12 AD differentiated wild-type or FOXA2 KO hESCs in the absence or presence of SHH. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Unpaired two-tailed Student's t test: ∗∗p < 0.01.
See also Figure S3.