Figure 7.
Generation of Distinct Neuronal Subtypes with AD and EB Paradigms
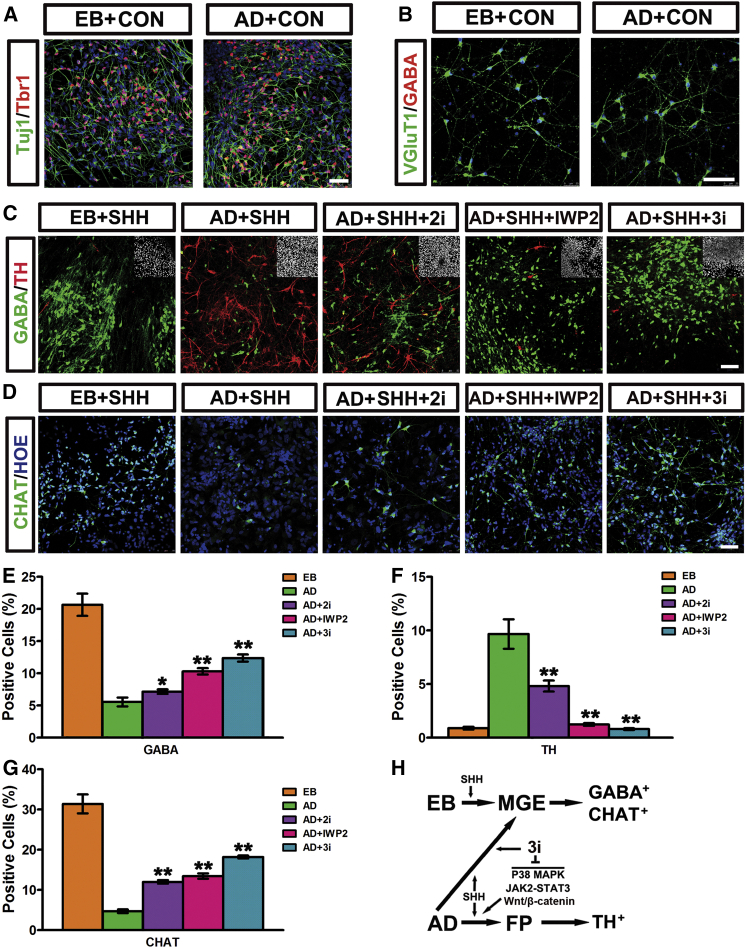
(A and B) Without SHH treatment, both EB and AD anterior-dorsal progenitors generate TUJ1+/TBR1+ (A) and VGluT1+/GABA− (B) cortical neurons at day 50 post differentiation. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(C and D) EB-MGE progenitors mostly generate GABA interneurons (C) and CHAT+ cholinergic neurons (D). AD-FP progenitors mostly generate TH+ DA neurons (C). Blocking p38, STAT3, and Wnts pathways generates more GABA and cholinergic but fewer DA neurons. Insets show Hoechst counterstaining of nuclei. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(E–G) Quantification of percentage of positive GABA (E), TH (F), and CHAT (G) cells in (C) and (D). Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Unpaired two-tailed Student's t test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
(H) Summary of strategies for differentiation of various ventral progenitors and related neuronal subtypes via EB and AD differentiation paradigms in combination with small molecules.
See also Figure S6.