Figure 1.
Experimental Overview for Profiling Molecular Mechanisms Governing In Vivo Tibialis Anterior Muscle Regeneration after Severe Trauma
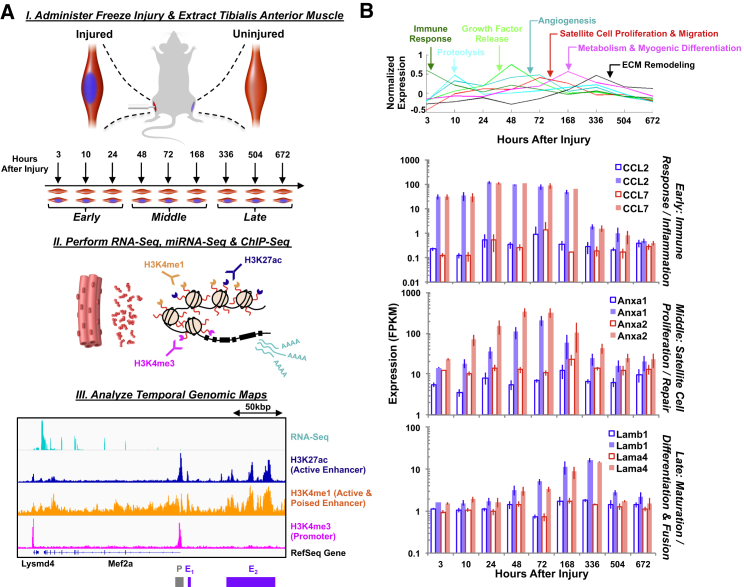
(A) Schematic diagram of injury model and process flow for chromatin and transcript extraction. A representative example of the Mef2a gene at 3 hr post injury is shown where the promoter (labeled P in gray) and enhancer regions (labeled E1 and E2 in purple) are depicted.
(B) (Top) Line plots of hierarchically clustered RNA-seq data through time revealed clusters up- and downregulated at different time periods that were associated with different stages of muscle repair and regeneration. (Bottom) Bar graphs of gene expression values of six different genes corresponding to different stages of the muscle regeneration process through time from left to right. Error bars represent 1 SD.