Fig. 3.
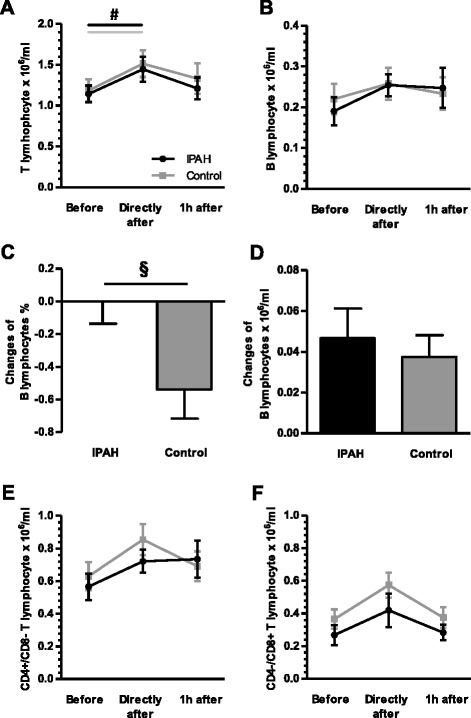
Exercise-induced changes in lymphocyte subsets: Exercise caused a transient significant elevation of T lymphocytes in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) and healthy subjects (a), but not in B lymphocytes (b). In the latter, however, exercise led to a relative reduction in healthy subjects but in IPAH patients, which was not observed for absolute numbers of B lymphocytes (c and d). Exercise provoked by a non-significant trend an elevation of CD4+/CD8- T helper and CD4-/CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IPAH and healthy subjects (e and f). CD = Cluster of differentiation. § p < 0.05 (t-test); # p < 0.05 (rANOVA)
