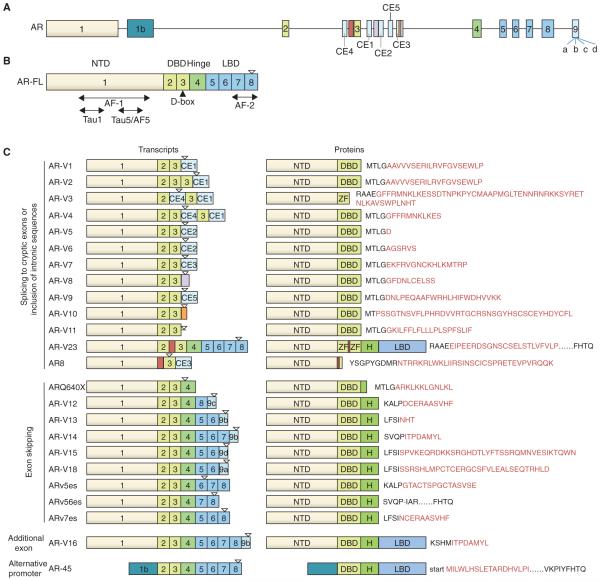
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the structure of AR-FL and AR-V transcripts and proteins.
A. AR gene structure with canonical exons and the cryptic exons (CE). B. AR-FL mRNA structure showing exons encoding the N-terminal domain (NTD; exon 1), DNA-binding domain (DBD; exons 2 and 3), hinge region (part of exons 3 and 4), and ligand-binding domain (LBD; exons 5-8). AF-1, Tau1, Tau5/AF-5, and AF-2 are activation function domains. Filled triangle depicts the D-box, which mediates AR-V/AR-V, AR-V/AR-FL, and AR-FL/AR-FL dimerization. C. mRNA and protein structures of AR-Vs. AR-V-specific peptide sequences are indicated in red, and the “-“ in ARv56es indicates a unique junction. Inverted open triangle depicts translation stop. Drawings are not to scale. Exon 9 harbors four cryptic 3’ splicing sites, and the corresponding cryptic exons are indicated as 9a, 9b, 9c, and 9d.