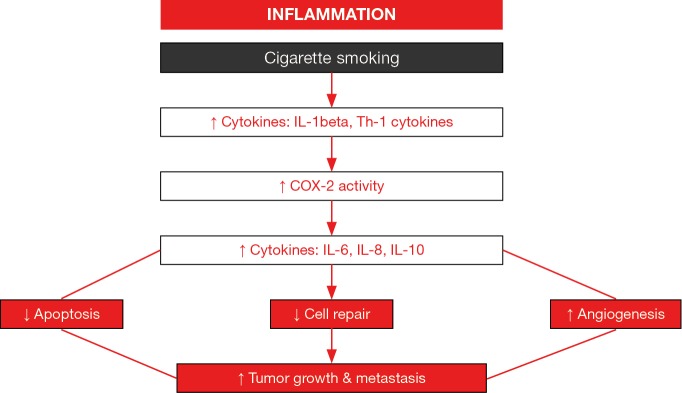
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the potential role of cytokines in tumor development in patients with underlying COPD. Cigarette smoking induces chronic inflammatory events characterized by the induction of several interleukins (IL), cyclooxygenase-2 activity, and cytokines. These inflammatory molecules interfere with key regulatory mechanisms such as cell death (apoptosis), cell repair, and angiogenesis, which contribute to the neoproliferative including tumor growth and metastasis.