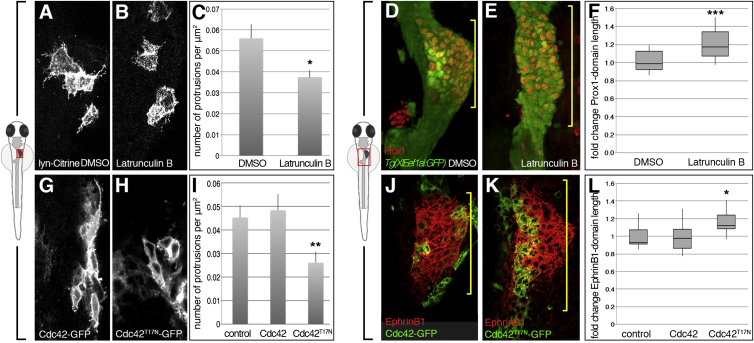
Figure 3.
Compromised Protrusion Formation Correlates with Liver Budding Defects
(A–F) Latrunculin B (0.1 μg/ml) treatment during liver budding (26–32 hpf) leads to significantly less hepatoblast protrusions (A–C; DMSO clones, n = 7; Lat B clones, n = 9, N = 1), and a significantly longer Prox1 domain (bracket) (D–F; DMSO, n = 23; Lat B, n = 13, N = 2).
(G–L) Hepatoblasts expressing Cdc42T17N-GFP during liver budding (26–32 hpf) form significantly less protrusions compared to controls and Cdc42-GFP (G–I; control clones, n = 10; Cdc42-GFP clones, n = 16; Cdc42T17N-GFP clones, n = 18, N = 1) and a significantly longer EphrinB1 domain (bracket) (J–L; control, n = 7; Cdc42-GFP, n = 18; Cdc42T17N-GFP, n = 16, N = 2). N indicates the number of experiments.
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.