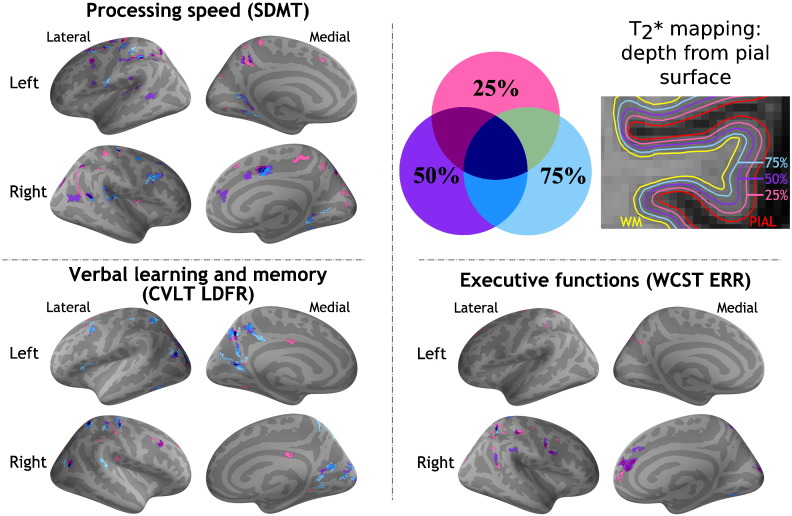
Fig. 2.
Cortical areas showing a significant correlation between quantitative T2* at 7 Tesla and neuropsychological performance at different cognitive domains in subjects with multiple sclerosis. Overlay of the general linear model (GLM) significance maps (p < 0.05 corrected for multiple comparisons) showing clusters with a correlation between q-T2* at 25%, 50%, and 75% depth from the pial surface and neuropsychological tests' scores. A negative correlation was found between cortical q-T2*, SDMT, CVLT LDFR scores (lower performance reflected in lower raw scores). A positive correlation was found between cortical q-T2* and WCST ERR (lower performance reflected in higher raw scores). Age, gender, education, WM lesion volume and cortical thickness at the vertex level were included as covariates of no interest in the model.
SDMT: symbol digit modalities test; CVLT LDFR: California verbal learning test long delayed free recall; WCST ERR: Wisconsin card sorting test total errors; WM: white matter; q-T2*: quantitative T2*.