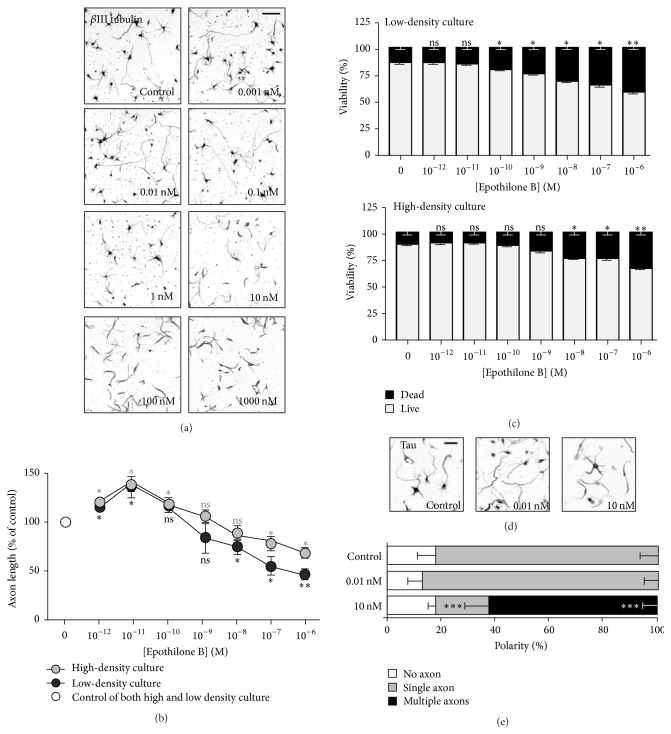
Figure 1.
Effects of epothilone B on axon growth and cell viability in embryonic cortical neurons. (a–e) Embryonic day 15.5 (E15.5) cortical neurons were plated at a low density (5 × 104 cells/1.9 cm2) or at high density (2 × 105 cells in 1.9 cm2) and cultured in the absence or presence of various concentrations of epothilone B, from 1 pM to 1 μM, as indicated. Low- and high-density cultures were fixed at 72 hr and 24 hr after plating, respectively, and subjected to immunostaining with anti-Tuj1 antibodies (a, b). Representative images ((a), inverted images from Tuj1 immunostaining; low-density culture) and quantification of axon length (b) are shown (gray, high-density culture and black, low-density culture). Cell viability was assayed by propidium iodide (PI) staining (c). To assess polarization, neurons treated with vehicle (control) or the indicated concentration (0.01 nM or 10 nM) of epothilone B were immunostained with anti-Tau antibodies (d, e). Representative images (d) and quantification of neuronal polarity (e) are shown. Scale bar, 50 μm. ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗ p < 0.001; ns, statistically not significant.