Figure 1.
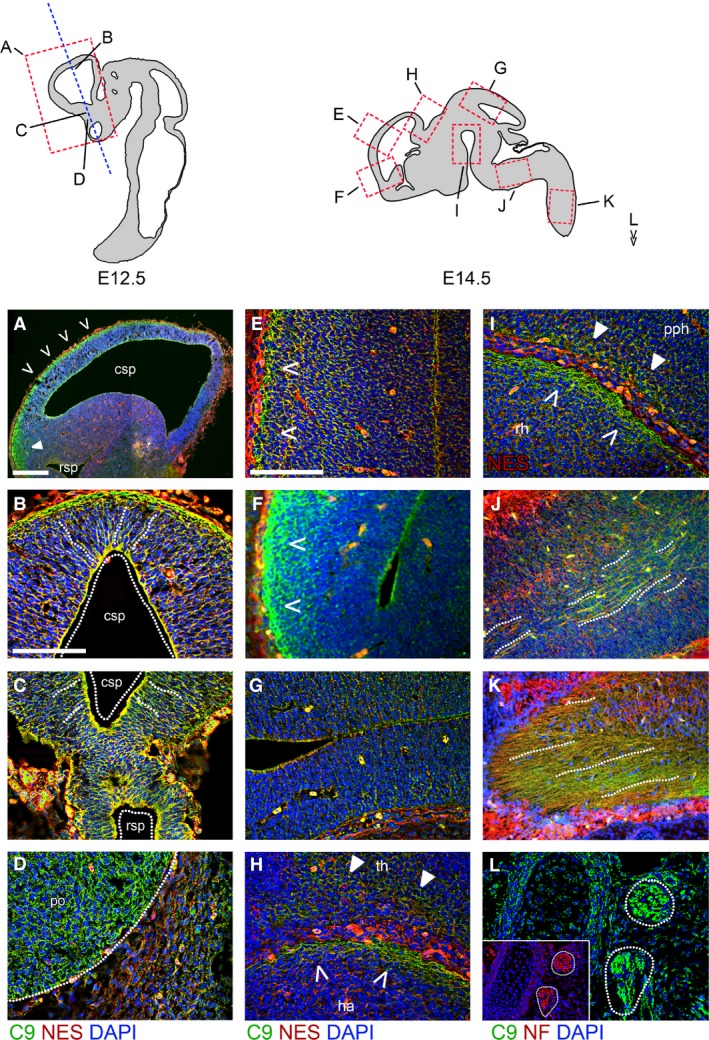
C9orf72 is present in the early embryonic brain and spinal cord. (A–D) Immunostaining for C9orf72 and nestin in E12.5 embryos in sagittal (A) and coronal (B–D) orientations. Strong C9orf72 staining can be seen in the dorsal pallium of the telecephalon (A), in the superficial layer of the rostral pallium (B) as well as in regions adjacent to the caudal secondary proencephalic ventricle (csp) in a radial arrangement spanning outwards (dotted lines). A similar pattern is seen in the caudal subpallium (C) adjacent to the rostral secondary proencephalic ventricle (rsp). C9orf72 is strongest in neuronal tissues, as shown by expression in the pre‐optic area (D, po) adjacent to non‐neuronal tissue. Immunostaining for C9orf72 and nestin (E–I) or neurofilament (J–L) in E14.5 brain. Expression is strongest in the superficial layers of the caudal rostral pallium (E) and pre‐olfactory pallium (F). This pattern of expression is not seen in the caudal midbrain tectum (G). Strong staining again is found in the superficial layer of the hippocampal allocortex (H, ha, open arrows) and spread in deeper layers of the adjacent thalamic tissue (th, closed arrows). Strong staining is also seen in the superficial layer of the rostral hypothalamus (rh) and prepontine hindbrain (pph) (I). C9orf72 can be found aligned with neurofilament‐positive tracts in the medulla (J) and spinal cord (K). C9orf72 and neurofilament are found together in the spinal ganglia (L). Scale bars: 100 μm.
