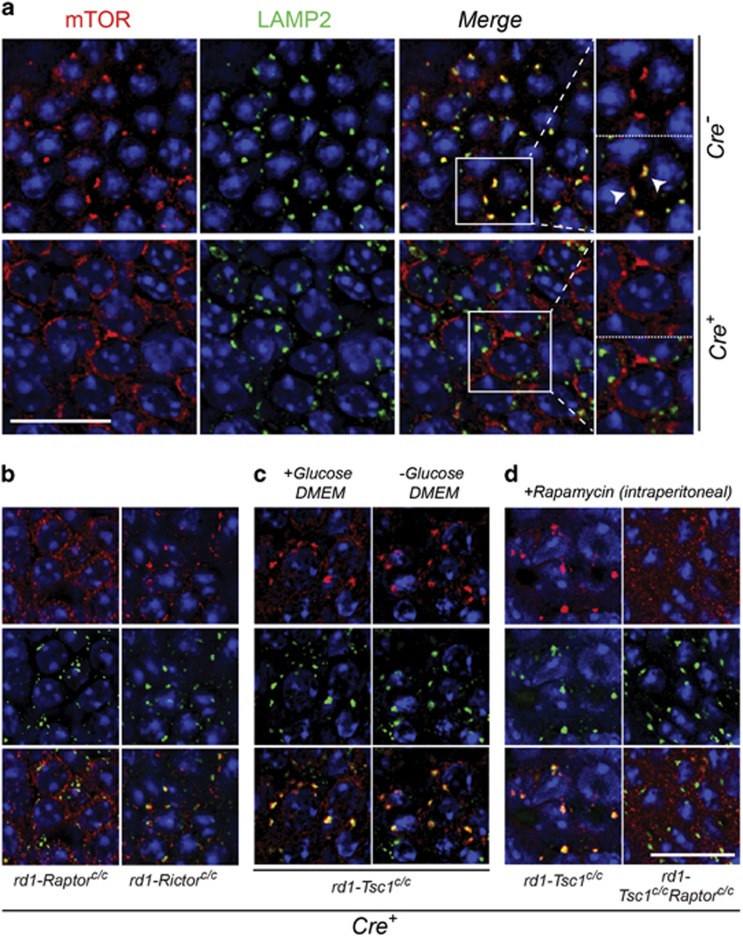
Figure 4.
mTOR and LAMP2 colocalization analysis reveals a shortage of amino acids upon Tsc1 loss in cones. Immunofluorescence analyses on retinal whole mounts of rd1-mutant mice harboring the conditional alleles indicated at 2 months of age. (a) Localization of mTOR to LAMP2-containing compartments in retinae of rd1-Tsc1c/c Cre− mice (arrowheads in higher magnification view). Localization is lost in Cre+ mice (lower row in a). Higher magnification view: the upper panel – mTOR; lower panel – mTOR and LAMP2. (b and c) Only Cre+ retinae of genotypes indicated are shown, with the upper row showing mTOR staining, middle row showing LAMP2 and bottom row showing both mTOR and LAMP2. (b) mTOR/LAMP2 colocalization is lost in rd1-Raptorc/cCre+ mice, but retained in rd1-Rictorc/cCre+ mice. (c) mTOR/LAMP2 colocalization in rd1-Tsc1c/cCre+ mice can be restored by incubating retinae in DMEM media with or without glucose for 2 h. (d) Systemic administration of rapamycin (intraperitoneal) also restores mTOR localization at the lysosome, but not in retinae from rd1-Tsc1c/cCre+mice upon concurrent removal of Raptor. Retinae were harvested 2 h post-rapamycin injection. In all panels, red staining indicates mTOR, green LAMP2 and blue nuclear DAPI. Scale bars: 20 μm. Higher magnification images in (a): × 1.5 original magnification