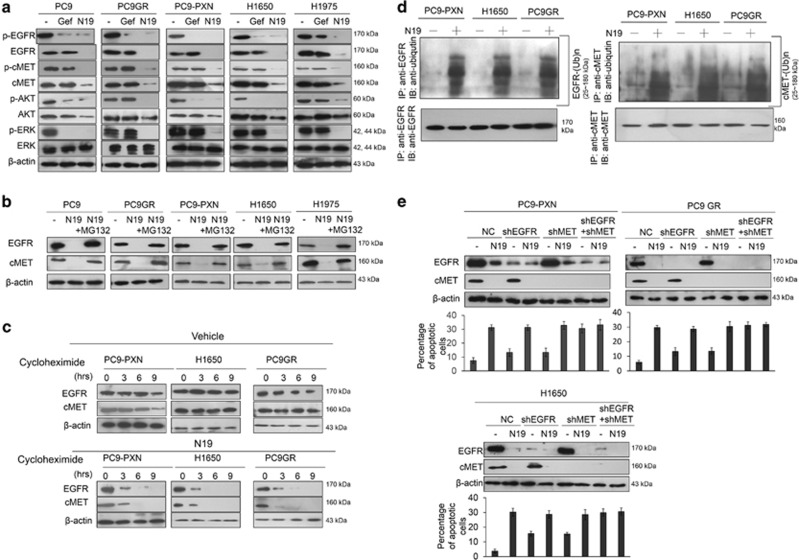
Figure 2.
N19 promotes ubiquitination to suppress the expression of EGFR and cMET proteins and their downstream signaling. (a) The effect of N19 on EGFR and cMET signaling. At 48 h after gefitinib (10 μM) or N19 (10 μM) treatment, the cell lysates were harvested and analyzed for the signaling alteration by western blot with indicated antibodies. (b) Inhibition of the proteasome pathway stabilized EGFR and cMET after N19 treatment. Cells were treated with or without MG132, or N19, or both, and analyzed by western blot. (c) N19 treatment decreased the half-life of endogenous EGFR and cMET proteins. PC9-PXN, H1650, and PC9GR cells treated with 100 μg/ml of cycloheximide for the indicated hours with or without 10 μM N19. The protein levels of EGFR and cMET were assessed by western blot. (d) The effect of N19 treatment on the polyubiquitination of EGFR and cMET. Cells were treated with N19 at 10 μM in PC9-PXN, H1650, and PC9GR cells, respectively, for 5 h. Polyubiquitination of EGFR and cMET were assessed by western blot in the IP. (e) The effect of EGFR or/and cMET knockdown on the apoptosis induced by N19 treatment. PC9-PXN, H1650, and PC9GR cells transfected with EGFR or/and cMET shRNAs were treated with 10 μM N19 for 24 h. The cell apoptosis was measured by annexinV-PI staining assay using a flow cytometry. All data were collected from three independent experiments. The mean value and S.D. were indicated as the column with error bars