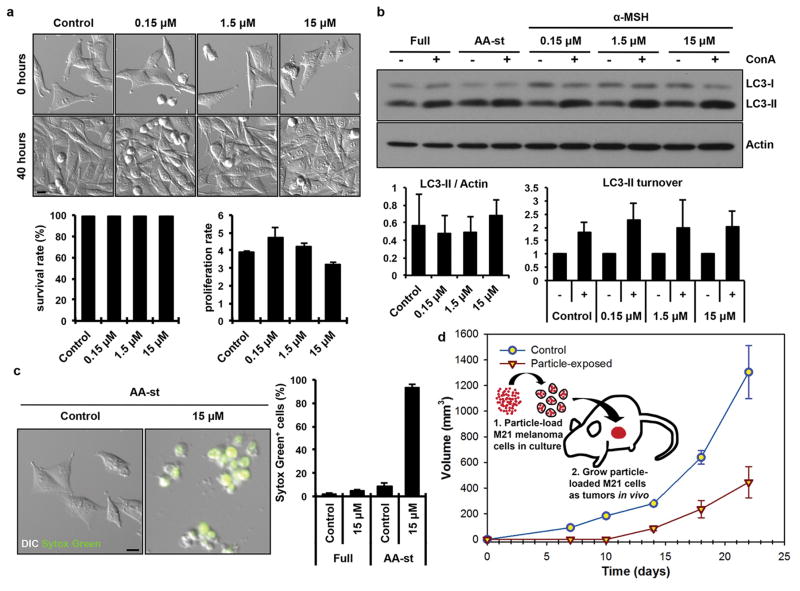
Figure 2. αMSH-PEG-C′ dot particles induce cell death in amino acid-deprived conditions.
a, Nanoparticles are well-tolerated in nutrient-replete media. Images show M21 cells treated with the indicated αMSH-PEG-C′ dot concentrations and cultured for 40 hours. Nanoparticles had no significant effect on cell survival (left graph) or cell proliferation (right graph), as quantified by time-lapse microscopy-based tracking of individual cell fates. Error bars indicate mean+/− standard error of the mean. N=3 biological experiments, with five independent fields of view for each. See Supp. Figure 6a,b for individual experimental values. Scale bar=10μm. b, Autophagy and lysosome function in nanoparticle-treated cells are unperturbed. Western blot shows LC3-I and –II in cells treated with increasing doses of αMSH-PEG-C′ dots for 24 hours compared to untreated (Full media) and amino acid-starved (AA-st) cells, in the presence (+) and absence (−) of the lysosome inhibitor concanamycin A (ConA, 1 hour at 100nM). Levels of LC3-II (left graph) are unaltered by nanoparticle treatment, and ConA-inducible LC3-II accumulation (right graph), a measure of autophagy flux, is similar between treated and untreated cells. Error bars indicate mean+/− standard error of the mean. N=3 biological replicates for each group. See Supp. Figure 6c,d for individual experimental values. c, Nanoparticle treatment induces cell death of M21 cells cultured in amino acid-free media. Images show live control cells and dead (Sytox green-positive) nanoparticle-treated cells in AA-st conditions. Scale bar=10μm. Graph shows percent Sytox green-positive cells in full media (Full) or AA-st conditions after 50 hours, as determined by time-lapse microscopy. Error bars indicate mean+/− standard deviation. N=4 for each group. Each replicate is from one biological experiment, quantified with five independent fields of view. d, M21 cells treated with 15μM αMSH-PEG-C′ dots in full media for 72 hours prior to create xenografts in immunodeficient (SCID/Beige) mice demonstrate growth inhibition (open inverted triangles) relative to untreated control cells (open circles). Schematic shows workflow, consisting of (1) particle-loading M21 melanoma cells, by treatment at 15uM for 48 hours in culture under full media conditions, and (2) injecting 5×106 particle-loaded M21 cells into mice to assay xenograft tumor growth versus control untreated cells. Data show mean tumor volume over 22 days of growth from three tumors per group. Error bars indicate mean+/− standard error of the mean. Particle-treated M21 cells showed statistically significant (p<0.001) growth inhibition compared with untreated control cells over the study interval. P-value is from a Wald test in a regression model estimated by generalized estimating equations to take into account the longitudinal nature of the data.