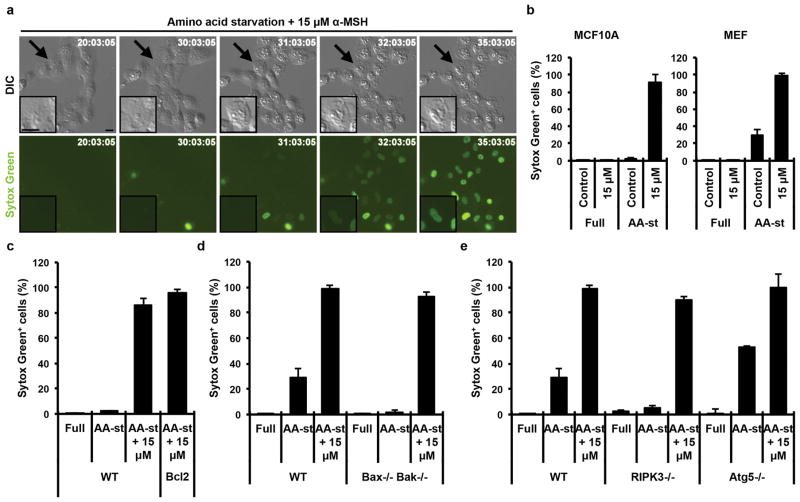
Figure 3. αMSH-PEG-C′ dot particle-induced cell death is not apoptosis, necroptosis or autosis.
a, MCF10A human mammary epithelial cells cultured in the absence of amino acids with 15μM αMSH-PEG-C′ dots undergo cell death after 30 hours with necrotic features. Insets show a dying cell indicated by an arrow. Fluorescence images show Sytox green-labeling of dead cell nuclei. Scale bar=10μm. b, Quantification of cell death (Sytox green +) in MCF10A and mouse embryo fibroblast (MEF) cultures in full media or amino acid-starved (AA-st) conditions in the presence or absence of 15μM αMSH-PEG-C′ dots, and after 40 hours (MCF10A) or 45 hours (MEF), as determined by time-lapse microscopy. Error bars indicate mean+/− standard deviation. N=5 per group. Each replicate is from one biological experiment, quantified with five independent fields of view. c–e, Cell death assays, as in (b), indicate that inhibition of apoptosis by Bcl2 overexpression in MCF10A (c), quantified after a 38 hour time-lapse experiment, or deletion of Bax and Bak in MEF (d), quantified after 45 hours, or inhibition of necroptosis by deletion of ripk3 in in MEF (e), quantified after 45 hours, or inhibition of autophagy by knockout of Atg5 in MEF after 45 hours (e) does not inhibit cell death induced by amino acid starvation and treatment with 15μM αMSH-PEG-C′ dots. Error bars indicate mean+/-standard deviation. N=5 per group. Each replicate is from one biological experiment, quantified with five independent fields of view.