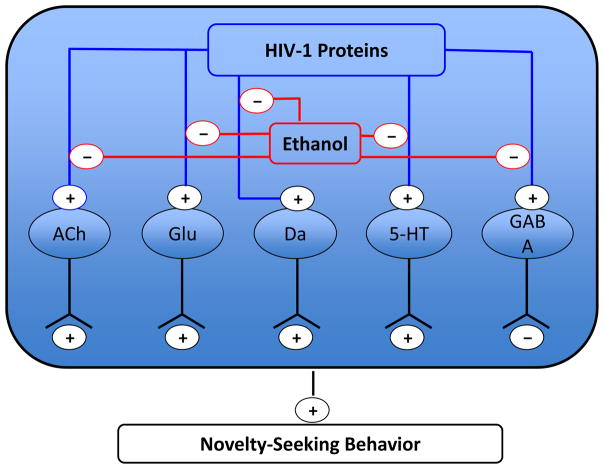
Figure 6.
Summary of the effects of HIV-1 proteins and chronic ethanol treatment on neurotransmitters in the NAc. (+) indicates an excitatory projection, and (-) indicates an inhibitory projection. We found that HIV-1 proteins enhance the signaling activity of the following neurotransmitters: acetylcholine (ACh), glutamate (Glu), dopamine (Da), serotonin (5-HT), and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Ethanol treatment interacted with HIV-1 proteins to produce decreased signaling activity of these five neurotransmitters. HIV-1 proteins alone and in the presence of ethanol led to greater novelty-seeking behavior.