Figure 1.
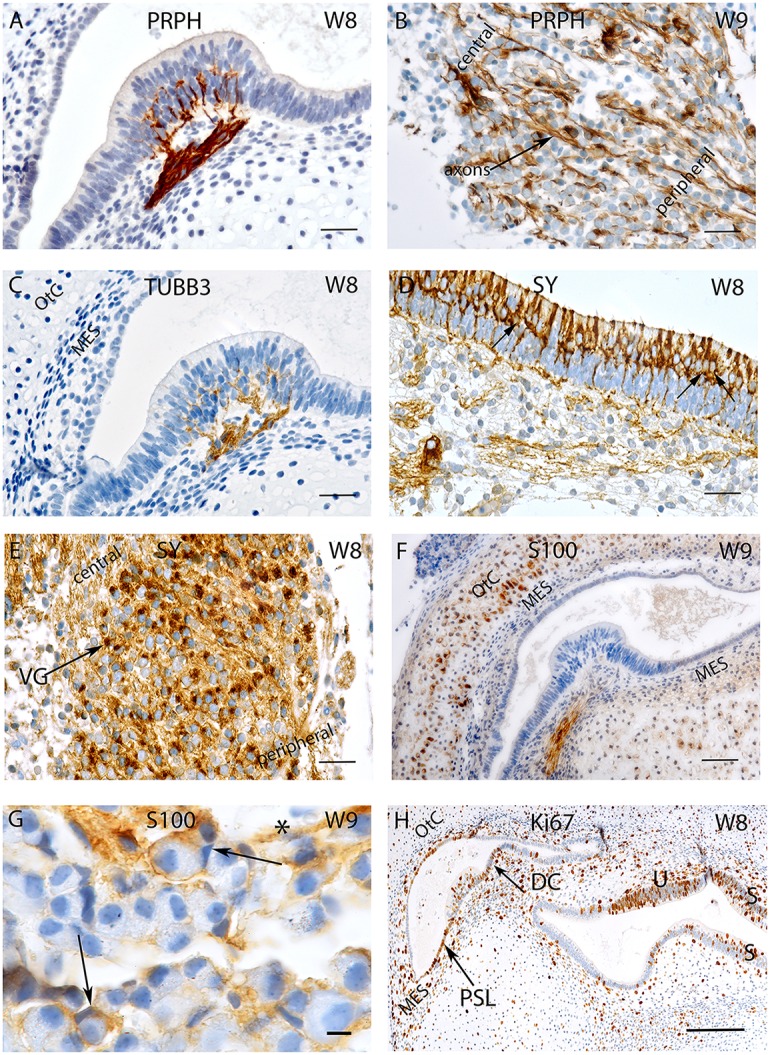
Sections of the developing VO between W8 and W9. (A) Peripherin staining in the Crista ampullaris (intensely stained Peripherin positive fibers are invading the sensory epithelium) and (B) the vestibular ganglion; peripheral as well as central axons of the vestibular nerves are immunoreactive. Fibers immunoreactive for TUBB3 are innervating the sensory epithelia of a crista ampullaris (C) by W8. The otic capsule (OtC) and the mesenchyme (MES) are all unstained. (D) Synaptophysin stained nerve fibers innervate the sensory epithelia of the developing utricule where immunoreactive hair cells and intensely stained nerve endings (arrows) are present. (E) Synaptophysin expression is also widespread in the vestibular ganglion (VG) cells with an apparent gradient in the staining intensity between the central and the peripheral regions of the ganglia. (F) S100 immunoreactivity is widespread in the ampullary crest with the nerve fibers projecting toward the sensory epithelia. The cytoplasm of the chondrocytes of the otic capsule (OtC) show immunoreactivity for S100. (G) S100 expression is also visible in the VG within stained putative Schwann cells (asterisk) and satellite glial cells (arrows) stained. (H) Ki-67 immunoreactivity is seen in few cells of the ampullary crest (H), within in the regions of the Planum semilunatum (PSL), dark cells (DC) of the cristae, sensory epithelium of the utricle (U), saccule (S) and the developing mesenchyme (MES). Scale bar: 12 μm (A–F,H), 10 μm (G).
