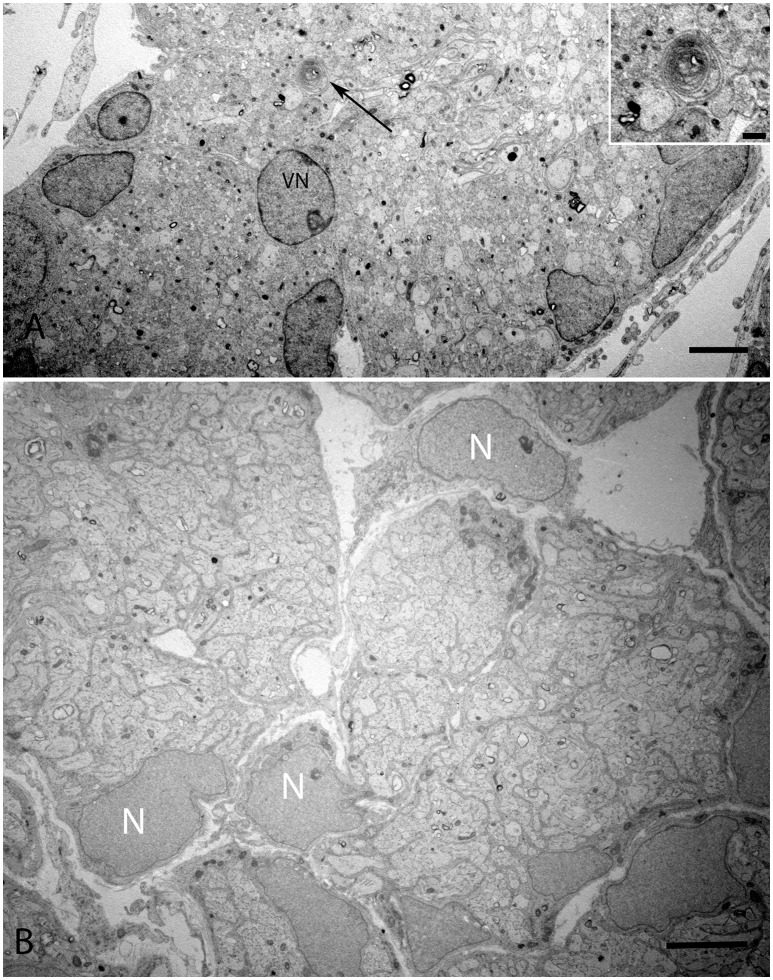
Figure 9.
Overview of the vestibular nerve close to the ganglion in the human fetal VO with the onset of myelin formation (arrow) visible in (A). Inset image exhibits the loose myelin structures. The vestibular neuron (VN) can clearly be distinguished by the nucleus structure, while other cell types possess high variability in cell nucleus structure. These cells surround nerve fibers, most of them are probably non-myelinating Schwann cells starting to wrap axons. (B) visualizes an adjacent portion of the vestibular nerve where the compartmentalization of the fascicles have already occurred with highly active nuclei (N) with no heterochromatin visible. Scale bar: 2 μm (A,B), 500 nm (A, inset.)