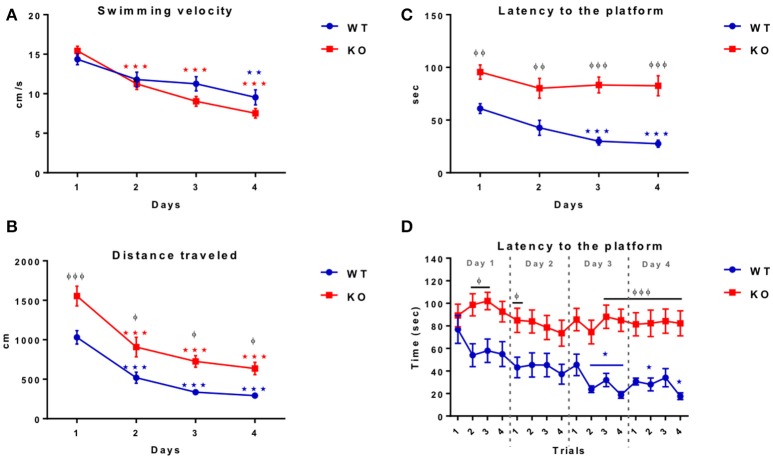
Figure 10.
Morris water maze training. (A) Shows the swimming velocity (cm/sec) of WT (blue; n = 14) and Fus1 1 KO (red; n = 19) over 4 days of training. Significance is determined by a change in velocity compared with day 1. One way RM ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post-hoc, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Both WT and KO decreased their swimming velocity. (B) Illustrates the swimming distance (cm) of WT (blue; n = 14) and Fus1 1 KO (red; n = 19) over 4 days of training. Significance is determined by a change in velocity compared with day 1. One way RM ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post-hoc, ***P < 0.001. Differences between groups shown as φP < 0.05, φφφP < 0.001, two way ANOVA. Both groups decreased their distance however, overall Fus1 KO traveled further across training days. (C) Demonstrates the latency to find the hidden platform by the WT (blue; n = 14) and Fus1 1 KO (red; n = 19) over 4 training days. (*) represents a significant decrease in latency (sec) to find the platform, one way RM ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post-hoc, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. groups are represented as (φ) φφP < 0.01, φφφP < 0.001, two way ANOVA. (D) This figure shows the latency (sec) of WT (blue) and Fus1 1 KO (red) to find the hidden platform in the NW quadrant over four consecutive trials performed during the four training days. The WT not Fus1 KO mice, were able to reduce their latency over trials; one way RM ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. Differences between groups were evident over training days, two way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post-hoc, φP < 0.05, φφφP < 0.001. WT were able to reduce their latency over the training sessions, but the Fus1 KO mice did not show differences between training days.