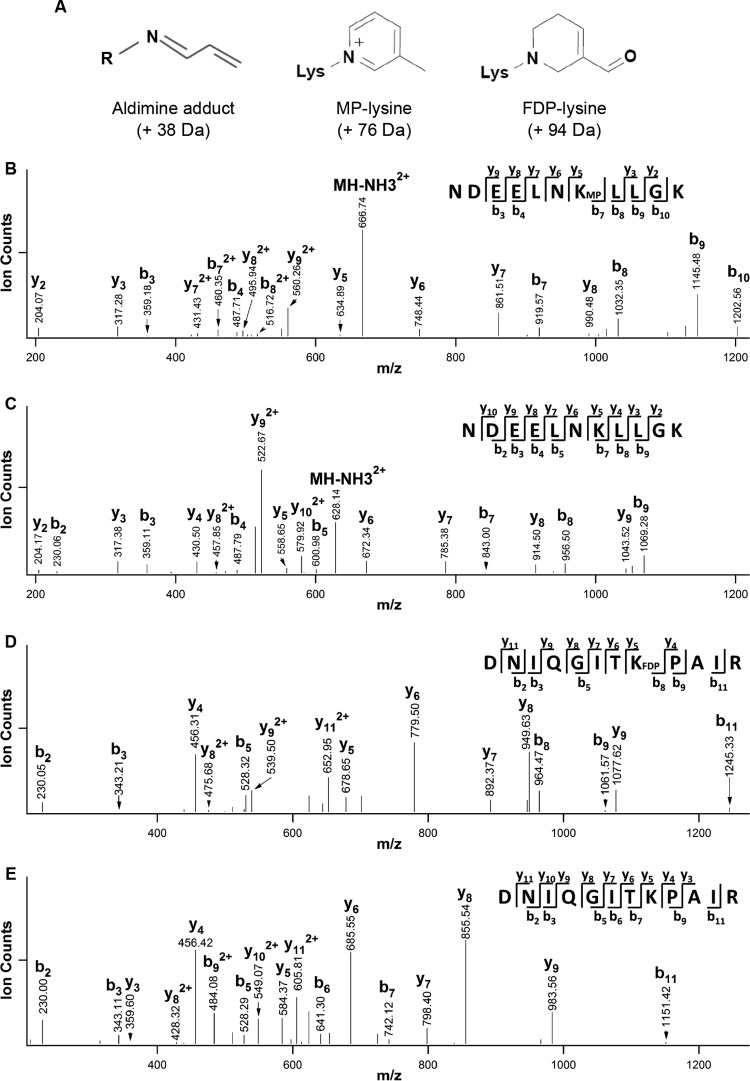
FIG 1.
Identification of Acr-modified lysines in recombinant H2A and H4 by LC-MS/MS. (A) Acr forms three major adducts with histone lysine residues: aldimine-modified lysine (A-lysine) with a mass addition of 38 Da, MP-modified lysine (MP-lysine) with a mass addition of 76 Da, and FDP-modified lysine (FDP-lysine) with a mass addition of 94 Da. These three types of mass addition can be detected by LC-MS/MS. (B, C) Identification of Acr-modified lysines in recombinant H2A by LC-MS/MS. Acr-treated H2A was separated by 14% SDS-PAGE and subjected to in-gel digestion with trypsin. The digestion products obtained were analyzed by LC-MS/MS to identify possible Acr-modified peptides. The peptide corresponding to Acr-modified 90NDEELNK(MP)LLGK100 (MH2+2 674.86) is shown in panel B. The observation of a series of y (y2, y3, y5∼y9) and b (b3, b4, b7∼b10) ions identified this peptide with a sequence of 90NDEELNK(MP)LLGK100, in which K96 has a mass addition of 76 Da, corresponding to an MP-modified lysine. (C) The unmodified peptide 90NDEELNKLLGK100 (MH2+2 636.84) from H2A identified by LC-MS/MS. (D, E) Identification of Acr-modified lysines in recombinant H2A and H4 by LC-MS/MS. (D) The peptide corresponding to Acr-modified 25DNIQGITK(FDP)PAIR36 (MH2+2 710.40) from H4 identified by LC-MS/MS. The observation of a series of y (y4∼y9, y11) and b (b2, b3, b5∼b7, b9, b11) ions identified this peptide sequence as 25DNIQGITK(FDP)PAIR36, in which K32 has a mass addition of 94 Da, corresponding to an FDP-modified lysine. (E) The unmodified peptide 2DNIQGITKPAIR36 (MH2+2 663.38) from H4 identified by LC-MS/MS.