FIG 3.
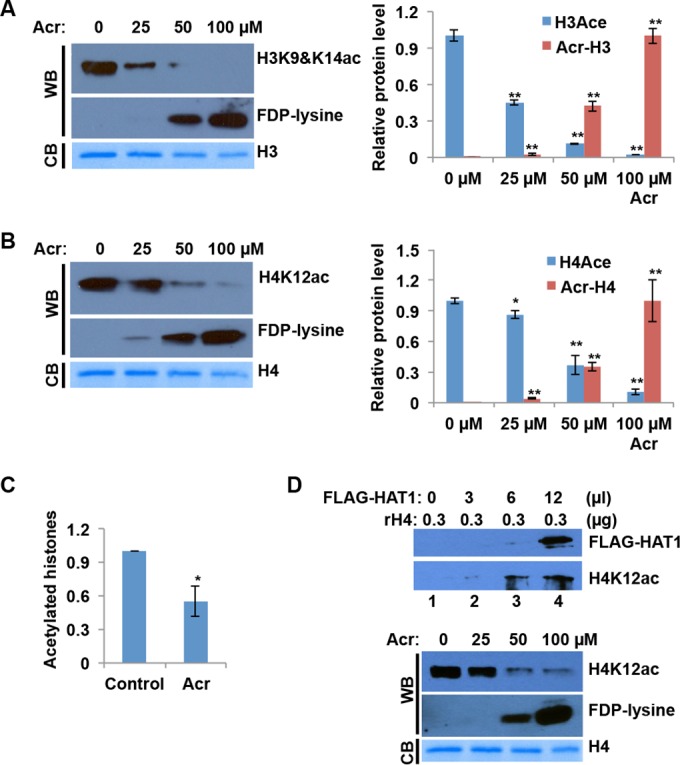
Acr-modified histones are resistant to acetylation. (A and B) Recombinant histone H3 (A) or H4 (B) was treated with Acr overnight prior to HAT reaction with CBP. The samples obtained were subjected to Western blot (WB) analysis with antibodies specific for H3K9&K14ac, H4K12ac, and FDP-lysine, which represent Acr-lysine adducts. Band intensities were quantified with ImageJ software. For comparison, the levels of H3ac/H4ac in lane 1 and Acr-H3/Acr-H4 in lane 4 were set as 1. The data shown are the mean values ± SD from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. CB, Coomassie blue. (C) Histone peptides were treated with Acr (0 and 100 μM) at 37°C overnight. After Acr was removed from the reaction mixture, Acr-treated and untreated histones were subjected to HAT assays with the EpiQuick HAT activity/inhibition assay kit. Cytosolic fractions from normal BEAS-2B cells were used as enzymatic sources. The data shown are the mean values ± SD from assays performed in triplicate. *, P < 0.05. (D, top) Recombinant histone H4 was treated with Acr overnight prior to HAT reaction with different dose of FLAG-HAT1. The samples obtained were subjected to Western blot analysis with antibodies specific for H4K12ac and FDP-lysine, which represent Acr-lysine adducts. (D, bottom) Experiments were carried out as described for panel B, except that FLAG-HAT1 replaced GST-CBP as an enzyme source.
