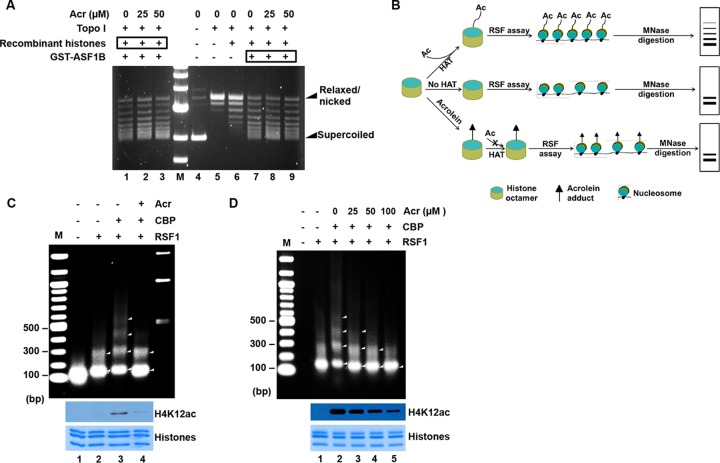
FIG 6.
Exposure of histones to Acr inhibits RSF-mediated chromatin assembly. (A) ASF1B-mediated plasmid supercoiling is not changed by Acr exposure. Plasmid supercoiling was not affected by the exposure of either histones or ASF1B to Acr. For lanes 1 to 3, reconstituted histone octamers were treated with Acr prior to reaction and then subjected to in vitro plasmid supercoiling assays. For lanes 7 to 9, GST-ASF1B was treated with Acr and then mixed with reconstituted histone octamers for plasmid supercoiling assays as described in Materials and Methods. A result representative of three independent experiments is shown. (B) Schematic representation of RSF chromatin assembly assays. (Top) Acetylation (Ac) of histones, especially H2A-H2B, is critical for the efficient formation of regularly spaced nucleosomes mediated by RSF, which generates nucleosomal DNA arrays when analyzed by partial MNase digestion. (Middle) With unacetylated histones, chromatin assembly is greatly inhibited, forming fewer regularly spaced nucleosomes, which are more accessible by MNase digestion, and generates only up-to-2-mer arrays. (Bottom) Since Acr-modified histones are resistant to acetylation by HAT (Fig. 3), the Acr-treated histones, similar to unacetylated histones, are assembled into chromatin efficiently by RSF, generating fewer DNA arrays when analyzed by partial MNase digestion. (C) Partial MNase digestion analysis of RSF assays with Acr-treated histones. Core histones (bottom, Coomassie blue staining) were treated with Acr (lane 4) or not treated with Acr (lanes 1 to 3) and subjected to acetylation in the presence (lanes 3 and 4) or absence (lanes 1 and 2) of CBP, generating acetylated or less acetylated histones, as evidenced by Western blotting with antibodies to H4K12ac (middle). These histones were then used in RSF chromatin assembly assays, followed by partial MNase digestion. DNA was extracted and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. While larger-than-4-mers of polynucleosomal DNA ladder were observed when acetylated histones were used (lane 3), only bands indicative of monomers and dimers were detected when Acr-exposed histones were used (lane 4). Lane M, DNA size markers. (D) Dose-dependent effects of Acr on RSF chromatin assembly. The assays were carried out as for panel C, except that different doses of Acr were used.