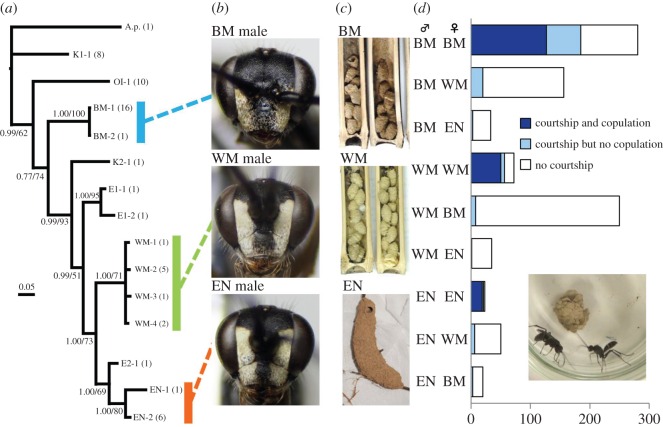
Figure 1.
Three cryptic species of the Auplopus carbonarius species complex. (a) Phylogenetic tree based on BI analyses of COI and 28S datasets combined (terminal taxa, haplotypes; numbers in parentheses, sample sizes). (b) Male heads of the three cryptic species, frontal view. (c) Nests of the three species. (d) Results of the mating experiments. The three wasp types are BM: black-mandibular type; EN: exposed nesting type and WM: white-mandibular type. A.p.: Auplopus pygialis (Pérez, 1905) (outgroup); K1: Korean type 1; OI: Okinawa Island type; K2: Korean type 2; E1: European type 1; E2: European type 2. The two numbers on each branch represent the Bayesian posterior probabilities (greater than or equal to 0.5) and ML bootstrap supports (greater than or equal to 50). The copulation success of males with conspecific females is significantly more frequent than that with non-conspecific females (for statistics, see the electronic supplementary material, figure S5). The courtship of males toward conspecific females is significantly more frequent than that toward non-conspecific females (for statistics, see the electronic supplementary material, figure S5).