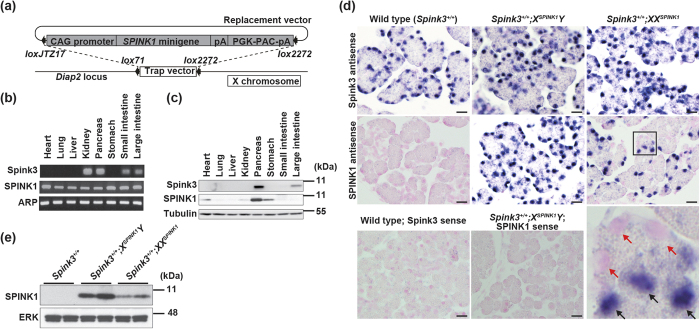
Figure 1. Generation of human SPINK1 X-chromosome knock-in (“X-SPINK1”) mice.
(a) A replacement vector containing SPINK1 minigene under the CAG promoter was introduced into Diap2 locus on the X chromosome by Cre-loxP technology. (b) RT-PCR analysis of Spink3 and SPINK1 mRNAs in various tissues of X-SPINK1 mice at 8 weeks. Acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein P0 (ARP), a “housekeeping” gene control. (c) The levels of Spink3 and SPINK1 proteins in various tissues of X-SPINK1 mice at 8 weeks (immunoblot). Representative of two independent experiments. (d) ISH analysis of SPINK1 mRNA expression in pancreas of mice of the indicated genotype at P0.5. Pancreatic tissue sections were hybridized with Spink3 (upper panels) or SPINK1 (middle panels) antisense riboprobes (blue stain). Nuclei stained with Nuclear Fast Red have a pink appearance. The bottom right panel is an enlarged image of the boxed area in the panel above. Black and red arrows indicate acinar cells with and without SPINK1 expression, respectively. The bottom left and center panels show ISH background control using SPINK1 and Spink3 sense riboprobes. Scale bars, 20 μm. Representative of two independent experiments. (e) Pancreas homogenates from mice of the indicated genotype at 8 weeks were analyzed by immunoblot analysis. In this and other figures, ERK or tubulin serve as loading control; each lane represents an individual animal; and the numbers to the right are protein molecular mass markers in kDa.