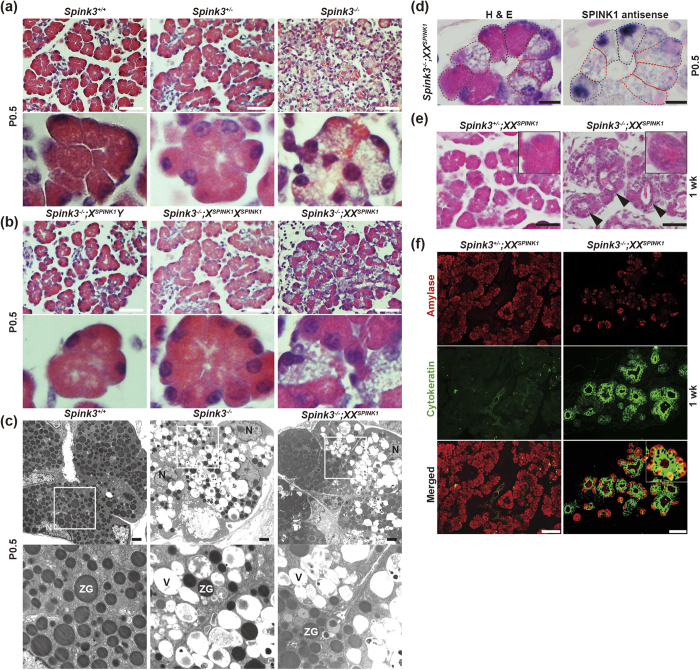
Figure 2. Crossing Spink3 deficient mice with X-SPINK1 rescues the resultant Spink3−/−;XXSPINK1 mice from perinatal lethality.
(a,b) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained pancreatic tissue sections from mice of the indicated genotype at P0.5. The lower rows in (a,b) show enlarged images of the upper panels. Scale bars, 50 μm. (c) Electron micrographs of pancreata of mice of the indicated genotype at P0.5. The lower row shows enlarged images of the areas designated by white boxes in the upper panels. ZG, zymogen granule; V, vacuole; N, nucleus. Scale bars, 2 μm. (d) Adjacent pancreatic tissue sections from Spink3−/−;XXSPINK1 at P0.5 were analyzed by H&E staining and ISH. Acinar cells expressing SPINK1 are delineated by black dashed lines, and those with no SPINK1 mRNA expression, by red dashed lines. Scale bars, 10 μm. (e) H&E staining of pancreatic tissue sections from mice of the indicated genotype at 1 week. Arrowheads indicate tubular structures. Insets show 2.5x-enlarged areas. Scale bars, 50 μm. (f) Cells positive for both amylase and pan-cytokeratin in pancreas of Spink3−/−;XXSPINK1 mice at 1 week. Pancreatic tissue sections from mice of the indicated genotype were immunostained using anti-amylase (red) or anti-pan-cytokeratin (green) antibodies. Scale bars, 50 μm.