Figure 2. DNGR‐1 can form reduction‐resistant dimers.
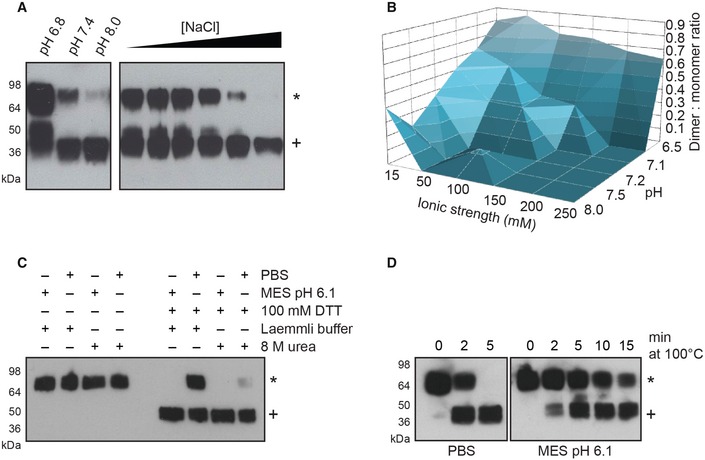
- 0.25 μg of purified long mouse DNGR‐1 ECD was diluted into 10 mM Tris buffer of the indicated pH (left panel) or into 10 mM Tris pH 7.4 buffer supplemented with increasing amounts of NaCl (1–250 mM; right panel), and reduction sensitivity of DNGR‐1 was assessed by reducing SDS–PAGE and Western blot.
- 0.25 μg of purified DNGR‐1 long mouse ECD was diluted into buffers of different pH and ionic strength, and its reduction sensitivity was assessed by reducing SDS–PAGE and Western blot. The intensity of bands corresponding to dimer and monomer was determined densitometrically, and the ratio was plotted as a function of buffer ionic strength and pH.
- 0.25 μg of purified long mouse DNGR‐1 ECD was diluted into PBS or 10 mM MES pH 6.1 buffer, and its reduction sensitivity was tested under mildly (Laemmli buffer) or strongly denaturing (8 M urea) conditions by reducing SDS–PAGE and Western blot.
- 0.25 μg of purified long mouse DNGR‐1 ECD was diluted into PBS or 10 mM MES pH 6.1 buffers, and its reduction sensitivity after different lengths of heat denaturation in Laemmli buffer was tested by reducing SDS–PAGE and Western blot.
