Fig. 1.
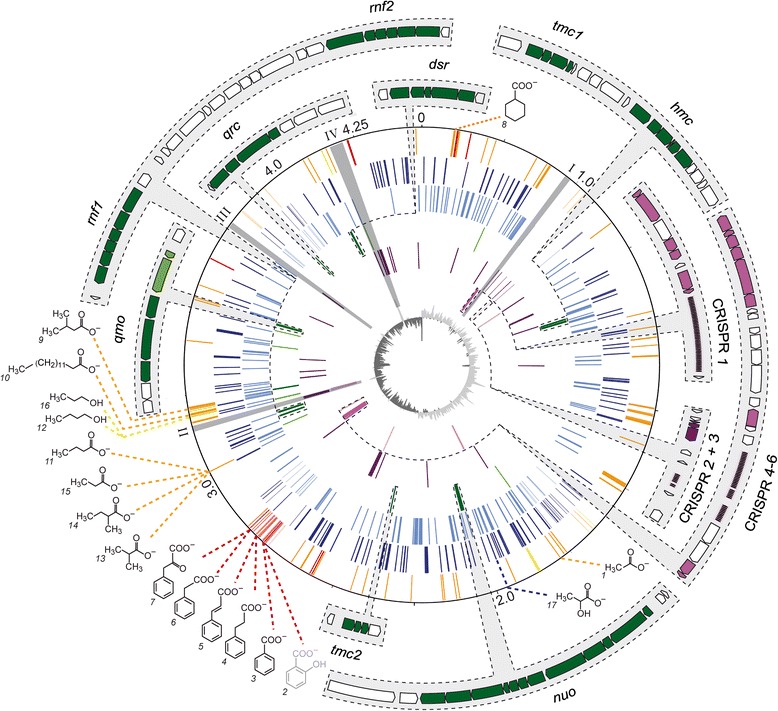
Structural representation of the chromosome of Desulfococcus multivorans. Location of gene clusters for aromatic and aliphatic compound degradation pathways are indicated by the corresponding chemical structure, with the respective names described in legend to Fig. 2 (grey: genome prediction; black: genome prediction confirmed by proteomics). The chromosomal location of redox complexes (dark green) and CRISPR-related and CRISPR-associated proteins (pink) are enlarged in the peripheral panel. Genomic islands I-IV are indicated by grey shading. Selected gene categories are represented by circles (from outside to inside): (i) aromatic compound degradation (red), fatty acid metabolism (orange) and alcohol dehydrogenases (yellow); (ii) other carbon metabolic functions (dark blue); (iii) signal transduction and transcriptional regulation (light blue); (iv) membrane-associated redox complexes (dark green) and sulfate reduction (light green); (v) transposases and mobile elements (purple); (vi) CRISPR-related and CRISPR-associated proteins (pink) and phage-related (light pink); (vii) GC skew (dark grey, below average; light grey, above average). The scale (Mbp) is indicated by the outer rim
