Figure 3. E1A 243R and E1A 1-80 promote association of MYC/MAX with the NuA4/Tip60 complex.
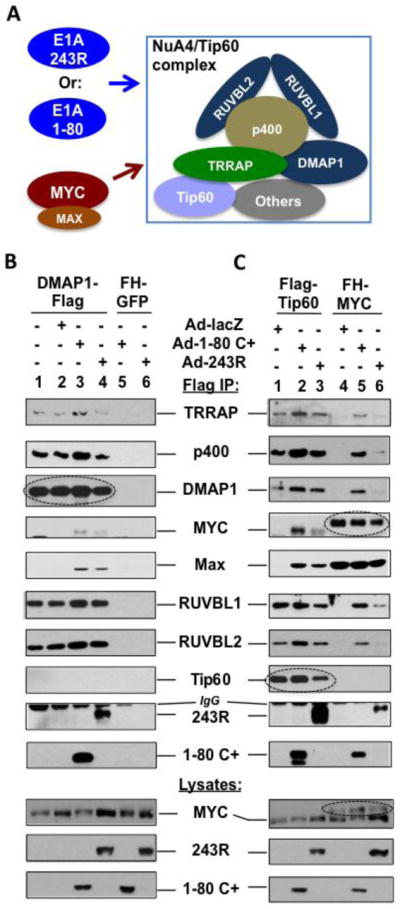
A. Experimental model. The relative position of each protein in the NuA4/Tip60 complex remains to be elucidated. B. Flag-DMAP1 interacts with E1A 1-80 and E1A 243R as well as components of the NuA4 complex identified by proteomic analysis. Flag-DMAP1 was expressed in HeLa cells using a lentivirus vector (lanes 1–4). The cells were then infected with Ad-lacZ (lane 2), Ad-E1A 1-80 C+ (lane 3), or Ad-E1A 243R (lane 4) as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Flag antibody beads and immunoprecipitates examined by Western blots with indicated antibodies. Lanes 5 and 6 are controls with HeLa cells expressing FH-GFP. Expressed DMAP1-Flag immunoprecipitated by the Flag antibody is indicated by a dashed oval. Expression of E1A 1-80 C+ or E1A 243R recruited MYC/MAX into the NuA4 complex (lanes 3 and 4). C. E1A 243R and E1A 1-80 promote the association of MYC/MAX with the NuA4/Tip60 complex. Experimental conditions are the same as in B, except that Flag-Tip60 (lanes 1–3) and FH-MYC (lanes 4–6) are expressed by lentivirus vectors. When the cells were not infected with an Ad vector (not shown), Flag-Tip60 and FH-MYC had the same patterns of binding as when Ad-lacZ was used (lanes 1 and 4, respectively). Expressed Flag-Tip60 or FH-MYC immunoprecipitated are indicated by a dashed oval to differentiate from cellular endogenous proteins. Expression of both E1A 1-80 C+ and E1A 243R recruited MYC/MAX into the NuA4/Tip60 complex when Flag-Tip60 was used for analysis (lanes 2 and 3). When FH-MYC was immunoprecipitated for analysis, E1A 1-80 and E1A 243R both enhanced the association of FH-MYC with the examined components of the NuA4/Tip60 complex (lanes 5 and 6).
