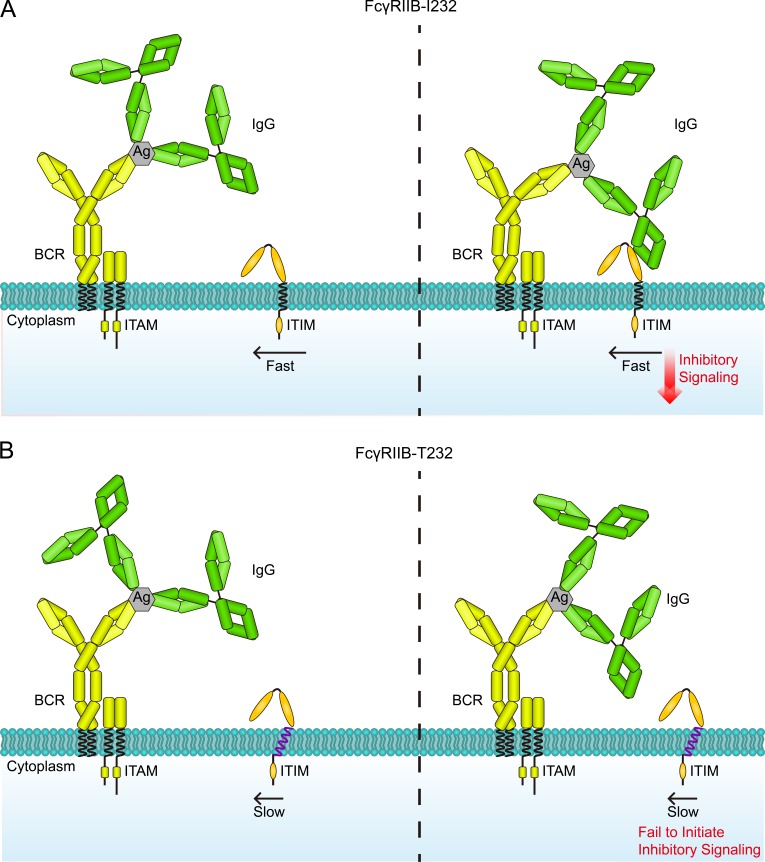
Figure 9.
A catch me if you can model to explain the function loss of FcγRIIB caused by the lupus-associated polymorphism I232T. (A and B) When B cells encounter the antigen (Ag) and IgG antibody ICs, BCR first interacts with antigens favorably to form BCR-IC microclusters, so as to initiate the BCR signaling cascades. Because of the weak affinity between FcγRIIB and the Fc portion of human IgG antibody, only the highly mobile FcγRIIB-I232 (A) could catch the IgG Fc portion in the IC microclusters through random diffusion, and its subsequent enrichment allows proper functioning by initiation of its inhibitory signaling. In contrast, the I232T polymorphism significantly impairs the mobility of FcγRIIB-T232 (B), which causes function loss by substantially reducing its chance to collide with the IgG Fc portion in the IC microclusters. ITAM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif; ITIM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif.