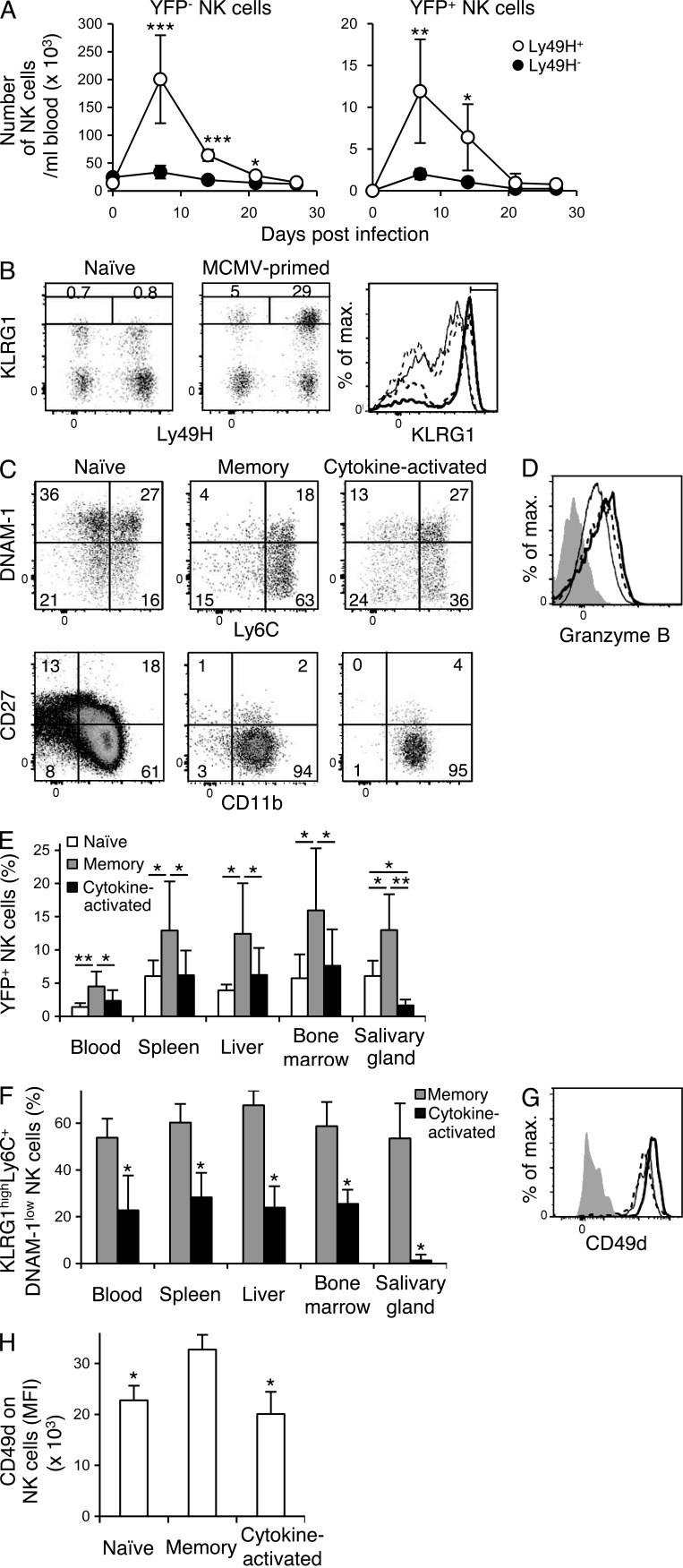
Figure 2.
NK cells differentiate into memory NK cells and cytokine-activated NK cells after MCMV infection. NKp46-CreERT2 Tg mice with a heterozygous Rosa26-YFP allele (A) or homozygous Rosa26-YFP alleles (B–H) were treated with tamoxifen on days 0–4 and infected or not with MCMV on day 0. (A) The number of YFP+ NK cells and YFP− NK cells in the blood over the course of infection. Data were pooled from two experiments (n = 7 in each group). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005 versus Ly49H− cells. (B) Expression of Ly49H and KLRG1 on YFP+ NK cells in the spleens of uninfected and infected mice on day 27 p.i. The percentages of Ly49H+KLRG1high NK cells and Ly49H−KLRG1high NK cells are shown. Expression of KLRG1 on YFP+ NK cells in the spleens of naive uninfected mice and on YFP+Ly49H+ memory NK cells and cytokine-activated YFP+Ly49H− NK cells from MCMV-infected mice. Bold solid lines, bold dashed lines, thin solid lines, and thin dashed lines represent memory NK cells, cytokine-activated NK cells, naive Ly49H+ NK cells, and naive Ly49H− NK cells, respectively. (C) Phenotype of YFP+ NK cells in the spleens of naive uninfected mice, and YFP+Ly49H+KLRG1high memory NK cells and cytokine-activated YFP+Ly49H−KLRG1high NK cells in the spleens of infected mice on day 25–32 p.i. (D) Expression of Granzyme B in YFP+ NK cells in the spleens of naive uninfected mice, and in memory YFP+Ly49H+KLRG1high NK cells and cytokine-activated YFP+Ly49H−KLRG1high NK cells in the spleens of infected mice on day 32 p.i. Bold solid lines, bold dashed lines, and thin lines represent memory NK cells, cytokine-activated NK cells, and naive NK cells, respectively. Filled histograms represent staining with an isotype-matched control Ig. Data are representative of more than five experiments (n = 2–6 in each experiment). (E) The percentages of YFP+ NK cells in naive uninfected mice on days 25–27 after tamoxifen treatment and the percentages of YFP+Ly49H+KLRG1high memory NK cells and cytokine-activated YFP+Ly49H−KLRG1high NK cells in the organs of tamoxifen-treated infected mice on days 25–27 p.i. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (F) The percentages of YFP+Ly49H+ NK cells and YFP+Ly49H− NK cells expressing a memory phenotype KLRG1highLy6C+DNAM-1low in the organs of tamoxifen-treated infected mice on days 25–27 p.i. Data are pooled from six experiments (n = 4–8 in each group). *, P < 0.01 versus memory cells. (G) Expression of CD49d on YFP+ NK cells in the blood of naive uninfected mice on day 25 after tamoxifen treatment and on YFP+Ly49H+KLRG1high memory NK cells and cytokine-activated YFP+Ly49H−KLRG1high NK cells in the blood of infected mice on day 25 p.i. Bold solid lines, bold dashed lines, and thin lines represent memory NK cells, cytokine-activated NK cells, and naive NK cells, respectively. A filled histogram represents staining with a control isotype-matched control Ig. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CD49d staining of NK cells are shown in H. Data are representative of two experiments (n = 4–6 in each group). *, P < 0.01 versus memory cells. P-values were calculated by a Student’s t test. Error bars show SEM.