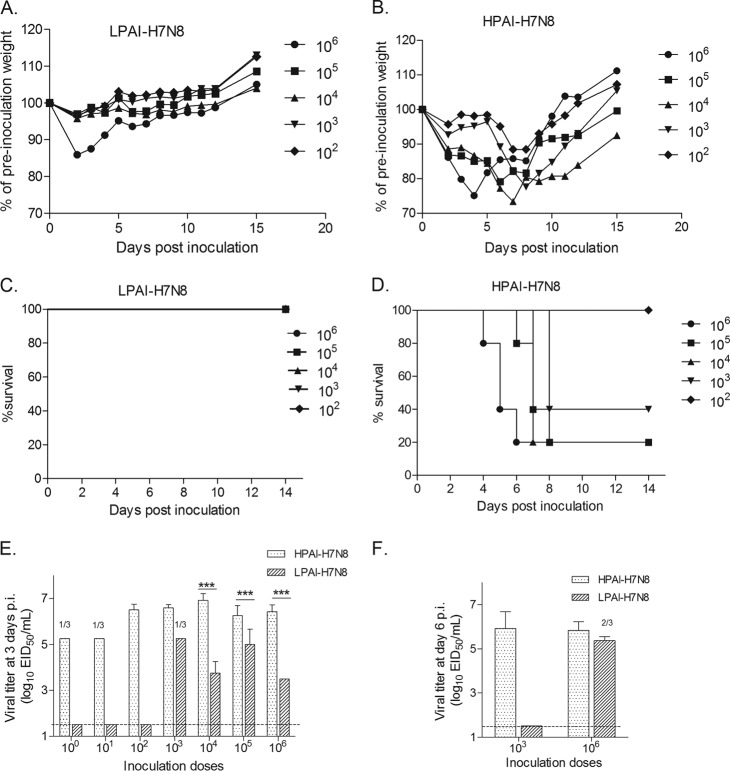
FIG 2.
H7N8 virus pathogenesis in mice. Groups of five BALB/c mice were i.n. inoculated with serial 10-fold dilutions (102.0 to 106.0 EID50) of LPAI (A, C) or HPAI (B, D) H7N8 viruses. The infected mice were observed and weighed daily until day 14 p.i., and any mouse with ≥25% weight loss or with severe signs of illness, including neurological symptoms, was euthanized. The mean percentages of preinoculation weight and survival for LPAI or HPAI H7N8 virus-infected mice are shown. (E) Groups of three mice were inoculated with 100.0 to 106.0 EID50 doses of HPAI or LPAI H7N8 virus and were euthanized on day 3 p.i. to determine viral titers in lung tissues. (F) Additional groups of three mice were inoculated i.n. with 103.0 or 106.0 EID50 of either H7N8 virus and were euthanized on day 6 p.i. for viral titration in lung tissues. The mean viral titers + SD in lung tissues on day 3 or day 6 p.i. are expressed as log10 EID50/ml of the clarified tissue homogenate supernatant. The dashed horizontal line indicates the detection limit of 1.5 log10 EID50/ml. If virus was not detected in 100% of mice in any particular group, the number of positive samples out of the total number of mice inoculated is shown. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA with GraphPad Prism if all three samples from each group were virus positive. ***, P < 0.001.