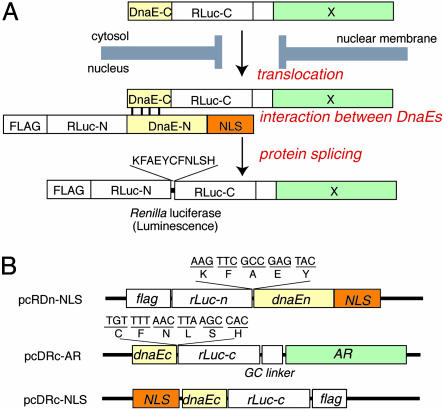
Fig. 1.
Basic strategy for the detection of AR translocation. (A) Principle for monitoring translocation of a particular protein (X) into the nucleus using protein splicing of split-Rluc. RLuc-N (1∼229 aa) is connected with DnaE-N (1∼123 aa) and NLS [(DPKKKRKV)3], which is predominantly localized in the nucleus. DnaE-C (1∼36 aa) is connected with RLuc-C (230∼311 aa) and a protein X, which is localized in the cytosol. When the tandem fusion protein consisting of DnaE-C, Rluc-C, and protein X translocates into the nucleus, the DnaE-C interacts with DnaE-N, and protein splicing results. Rluc-N and -C are linked by a peptide bond, and the reconstituted Rluc recovers its bioluminescence activity. FLAG means epitope (DYKDDDDK). (B) Schematic structures of cDNA constructs. All italics mean the genes of their corresponding proteins. Additional sequences at the boundaries between rLuc and dnaE are shown under the bars. GC linker, cDNA sequence of amino acids GGGGSG.