FIG 4.
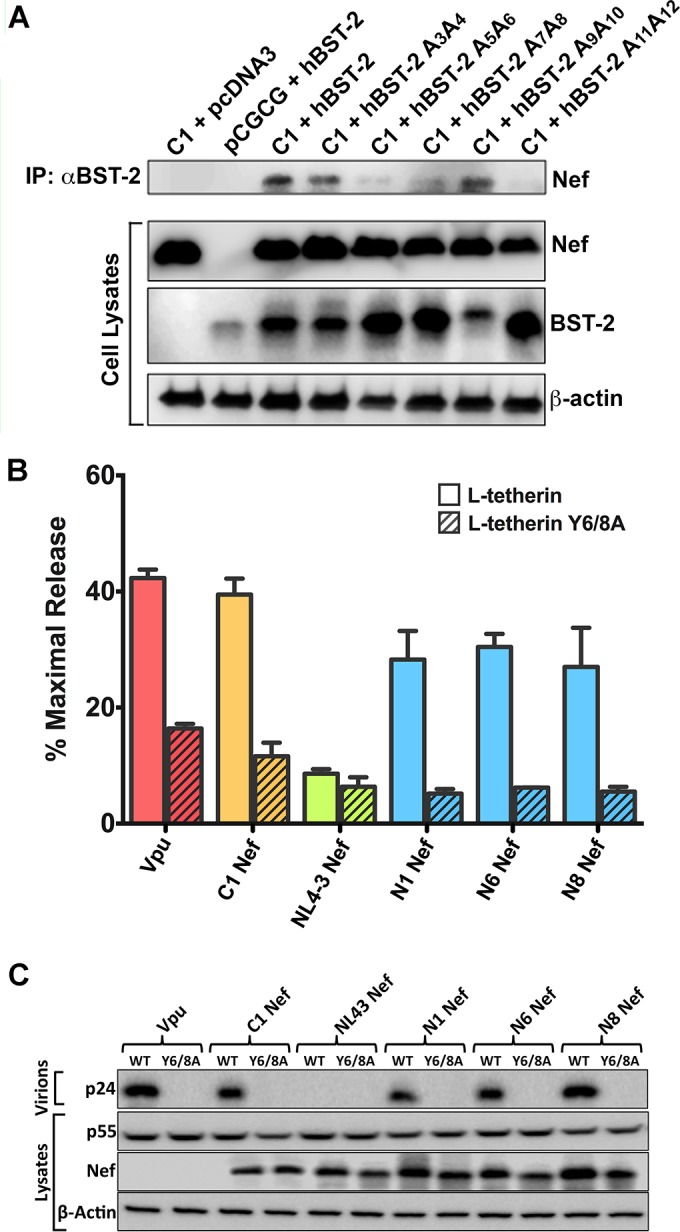
C1 Nef physically interacts with residues at the N terminus of human tetherin. (A) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with constructs expressing C1 Nef and either wild-type (WT) human tetherin (hBST-2) or tetherin mutants with alanine substitutions at the indicated positions in the N terminus of the protein. As controls, cells were also transfected with constructs expressing C1 Nef and an empty vector control for tetherin (pcDNA3) or human tetherin and an empty vector control for Nef (pCGCG). Whole-cell lysates and proteins immunoprecipitated (IP) by using an antibody to tetherin were separated by SDS-PAGE on 8% polyacrylamide gels and transferred onto PVDF membranes. Membranes were probed with antibodies to tetherin and to a Myc epitope tag appended to the C terminus of Nef. As a control for sample loading, the cell lysate membranes were also stripped and reprobed with an antibody to β-actin. (B and C) The indicted HIV-1 group M Nef proteins and HIV-1 NL4-3 Vpu were tested for their ability to rescue virus release for HIV-1 NL4-3 Δvpu Δnef in HEK293T cells cotransfected with constructs expressing L-tetherin or L-tetherin Y6/8A. The accumulation of HIV-1 p24 in the cell culture supernatant was measured by antigen capture ELISA (B), and the amounts of p24 in culture supernatants versus Nef and p55 Gag in cell lysates were compared by Western blot analysis (C).
