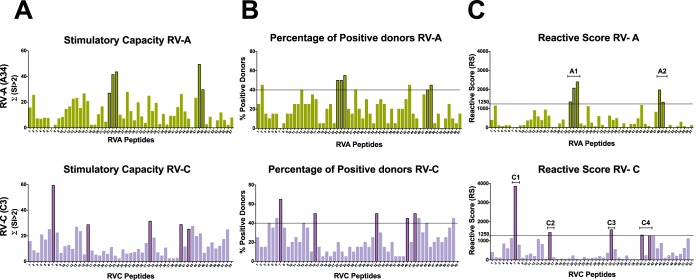
FIG 1.
Identification of T-cell epitopes in the VP1 capsid protein of RV-A (A34) and RV-C (C3) through in vitro stimulation of PBMCs with overlapping synthetic peptides from 20 donors and analysis of T-cell proliferation using a [3H]thymidine incorporation assay. The horizontal lines represent the thresholds used as selection criteria for immunodominance (RS ≥ 1,250 and percent positive donors ≥ 40%). (A) Stimulatory capacities given by the sum of SI values of >2 for each individual peptide. (B) Percentage of positive donors (donors presenting mean SI of >2) for a given peptide. (C) RS given by the product of the stimulatory capacity (panel A) multiplied by the percentage of positive donors (panel B) showing 5 immunodominant peptides for each RV-A and RV-C genotype tested: RVA-23, RVA-24, RVA-25, RVA-48, and RVA-49 and RVC-7, RVC-16, RVC-32, RVC-40, and RVC-42. While the RV-A response is focused on only two regions of VP1 (A1 and A2), the RV-C response is broad, with epitopes scattered throughout the protein (C1, C2, C3, and C4 regions).