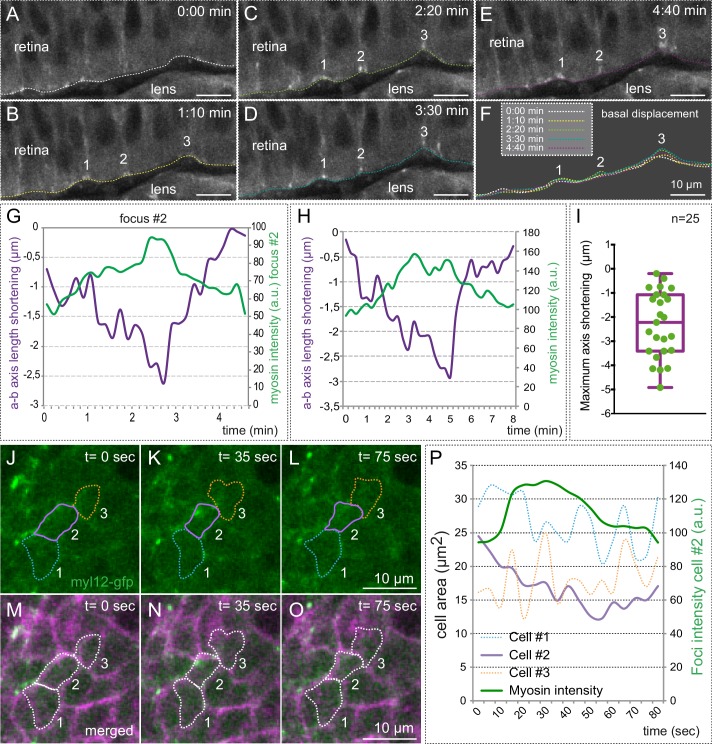
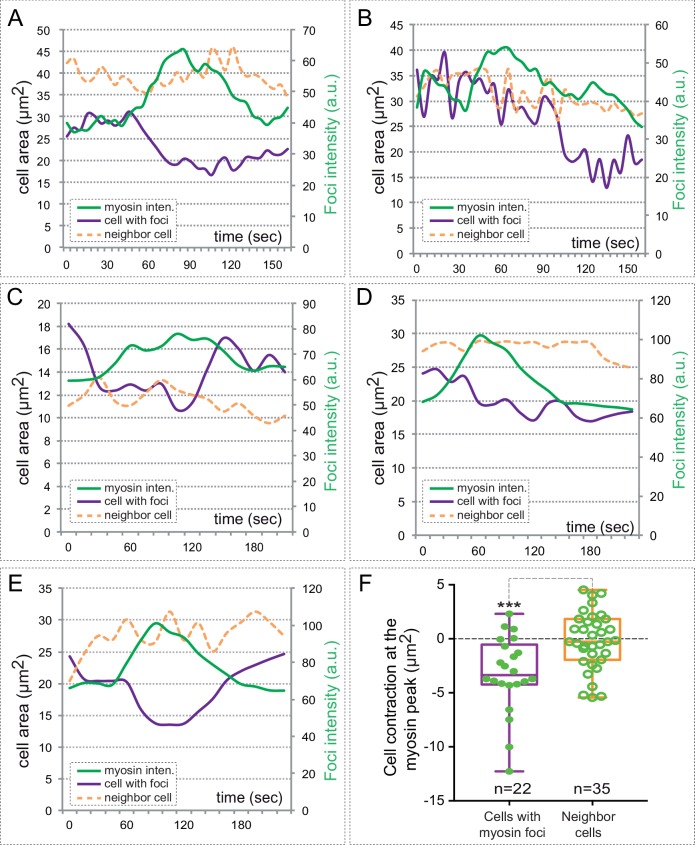
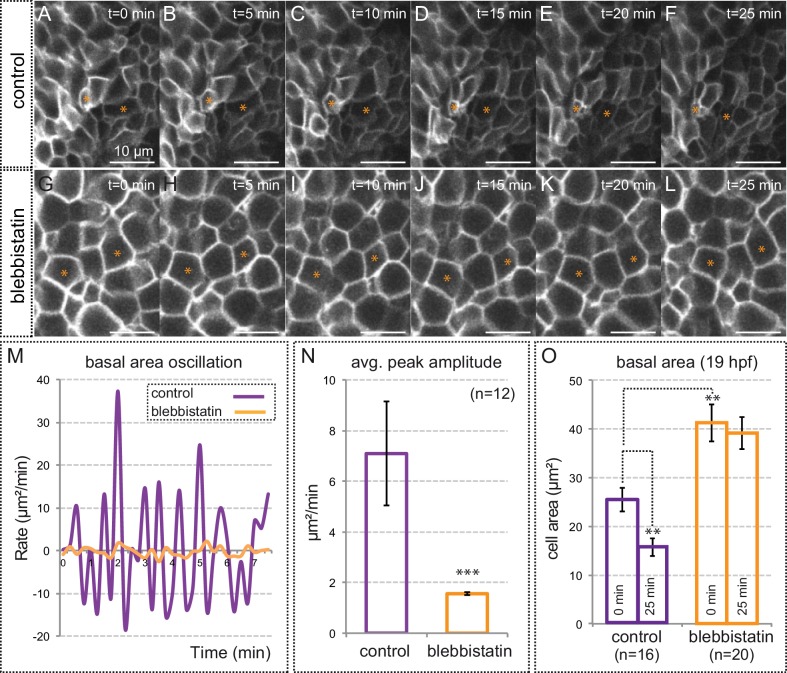
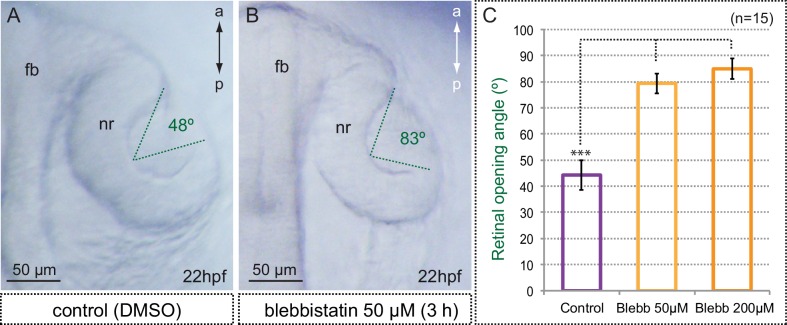
Figure 6. Myosin accumulation correlates with basal membrane displacement.
(A–E) Time series of optical sections from tg(actb1:myl12.1-eGFP) embryos show discrete myosin foci (labeled 1, 2, 3) and basal surface displacement. (F) Basal edges were color-coded for each time point and overlapped to illustrate the transient indentations of the basal surface associated to myosin foci. (G–H) Quantitative recording over time of myosin intensity and apico-basal axis shortening for a couple of representative foci. The focus in G is #2 in A–F. (I) Box plot showing the maximum shortening of the a-b axis for 25 foci from 12 different retinas. (J–O) Correlative analysis of basal area (revealed by lyn-tdTomato) and myosin dynamics is shown for three neighbor cells (color-coded). (P) Quantitative analysis of cell area changes and myosin intensity for the three neighboring cells. Note that only the cell accumulating myosin contracts. Scale bars =10 µm.