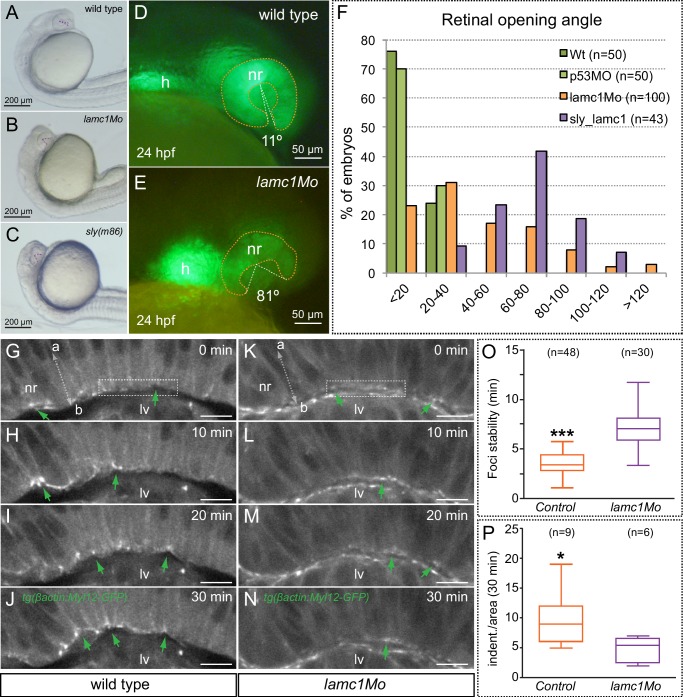
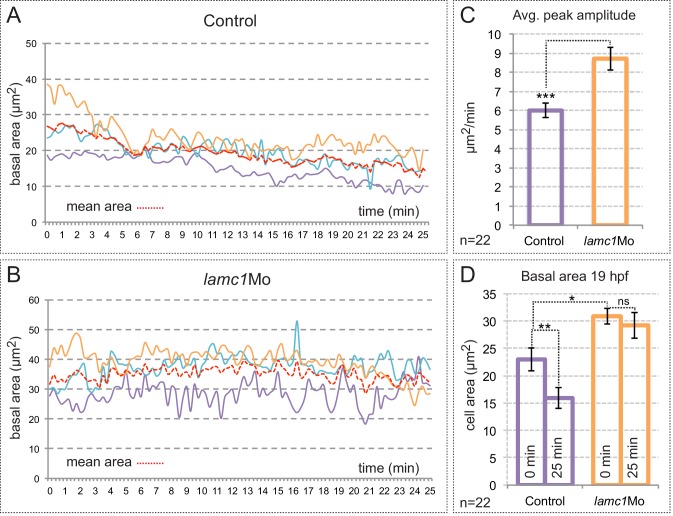
Figure 7. Optic cup folding, basal contractility and myosin dynamics depend on lamc1 function.
(A–C) General embryo morphology for wild type, lamc1 morphants and sly (lamc1-/-) mutants at 24 hpf. Retinal opening is indicated with a dashed line. (D–E) Retinal morphology in tg(vsx2.2:GFP-caax) both wild type and lamc1Mo-injected embryos, at 24 hpf. Ventral opening angle (white) and retinal contour (orange) are indicated with dashed lines. (F) Frequency distribution of retinal opening angles is shown for controls (either wild type or p53Mo-injected), lamc1Mo injected, or sly mutants. (G–N) Time-lapse analysis of tg(actb1:myl12.1-eGFP) wild type and lamc1Mo-injected embryos show dynamic accumulation of myosin foci (green arrows) at the basal surface. (O) Analysis of myosin foci reveals that they are significantly more stable in lamc1Mo-injected embryos (T-test). (P) The box plot shows that transient indentations of the basal surface are significantly diminished in lamc1Mo-injected embryos (T-test). h = heart; nr = neural retina; lv = lens vesicle. Scale bars = 200 µm in A–C, 50 µm in D–E, and 10 µm in G–N.