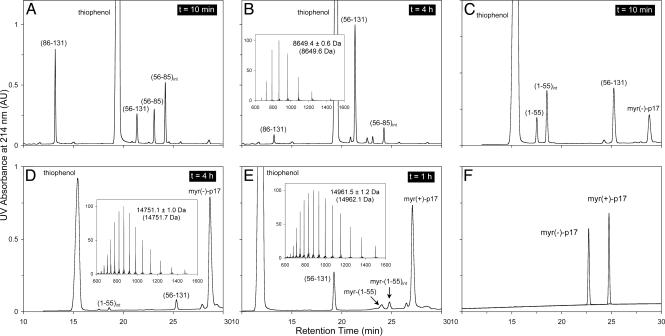
Fig. 2.
Analysis of the synthesis and native chemical ligation of myr(–)-p17 and myr(+)-p17. (A and B) Native chemical ligation of peptide fragments (56–85) and (86–131) monitored by analytical C18 RP-HPLC (5–65% solvent B over 30 min) at different time intervals. (C and D) Ligation of peptide fragments (1–55) and (56–131) monitored by HPLC (20–45% solvent B over 30 min) at 10 min and 4 h. (E) Ligation of peptide fragments myr-(1–55) and (56–131) monitored by HPLC (25–50% solvent B over 30 min) at 1 h. (F) Folded and purified HIV-1 p17 and its myristoylated form analyzed by C18 RP-HPLC (5–65% solvent B over 30 min). The molecular masses determined by electrospray ionization MS for the three ligation products, H-Cys(Acm)-(57–131)-OH, myr(–)-p17, and myr(+)-p17, were in agreement with the expected values (in parentheses) calculated based on the average isotopic compositions of the peptides. Finally, the three transient ligation intermediates, (56–85)int, (1–55)int, and myr-(1–55)int, were the products derived from a nucleophilic substitution reaction of corresponding peptide thioesters with the catalyst thiophenol.