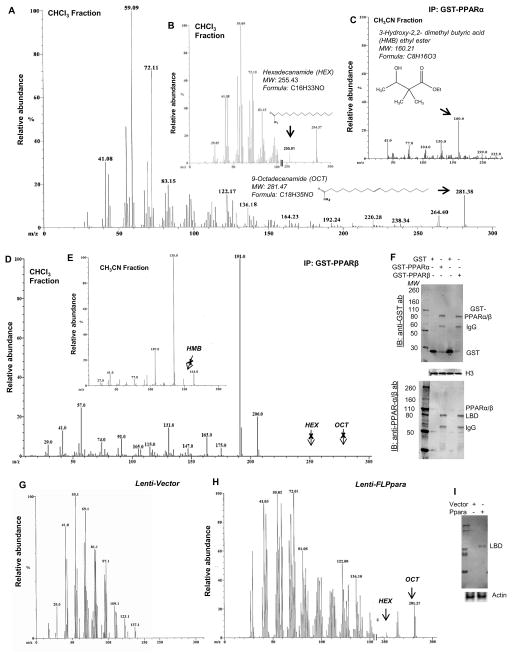
Figure 2. Identification of endogenous iigands of PPARα in the mouse brain hippocampus.
GC-MS analyses of chloroform- (A & B) and acetonitrile- (C) reconstituted nuclear extracts of WT hippocampus after pulling down with GST-PPARα-LBD. Similar GC-MS analyses were performed in chloroform (D) and acetonitrile (E) reconstituted nuclear extracts after pulling down with GST-PPARβ-LBD. F) The immunoblot analyses of eluate collected from glutathione column probed with anti-GST antibody (upper panel), and anti-PPARα or anti-PPARβ antibodies (lower panel). Histone 3 (H3) immunoblot was performed in the nuclear lysate (input) to show the purity of the nuclear extract (middle panel). For raw uncut blots, please see Supplementary Figure 13B. GC-MS analyses of the chloroform-extracted nuclear fraction of lenti-vector- (G) and lenti-PPARα- (H) transduced Ppara-null hippocampal neurons. I) Neuronal extracts infected with lenti-vector and lenti-PPARα were analyzed for PPARα and then normalized with actin. For raw uncut blots, please see Supplementary Figure 13C. Results were confirmed by three independent experiments.