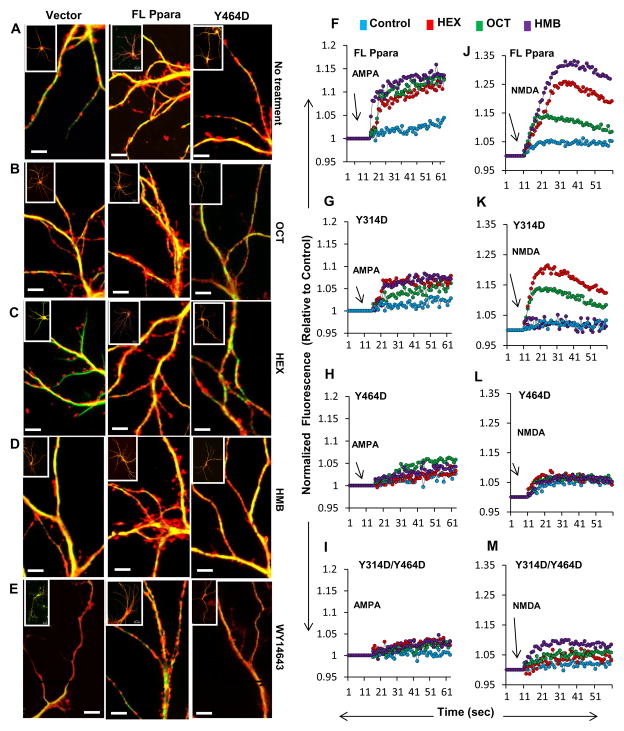
Figure 6. Effect of hippocampal ligands of PPARα on morphological plasticity and calcium oscillation in hippocampal neurons.
Ppara-null hippocampal neurons were transduced with lentivirions containing GFP (vector), FL-Ppara, and Y464D-Ppara for 48 h followed by treatment with vehicle (DMSO) (A), OCT (B), HEX (C), HMB (D), and WY14643 (E) for 24 h. Then neurons were stained for phalloidin to measure spine density. Scale bar = 20 μm. AMPA-driven calcium influx was measured in OCT (red), HEX (green) and HMB (purple)-treated Ppara-null hippocampal neurons transduced with lentivirions containing FL-Ppara (F), Y314D-Ppara (G), Y464D-Ppara (H), and Y314D/Y464D-Ppara (I). All neurons were treated with 50 μM of NMDA receptor antagonist N20C to inhibit passive calcium flow through NMDA receptor. (J–M) Similarly NMDA-driven calcium influx was measured in the lentivius-infected Ppara-null hippocampal neurons in the presence of different endogenous ligands. In these cases, Naspm-HCl was treated to stop the passive flow of calcium currents through AMPA receptor. Results are mean of three independent experiments.