FIGURE 1.
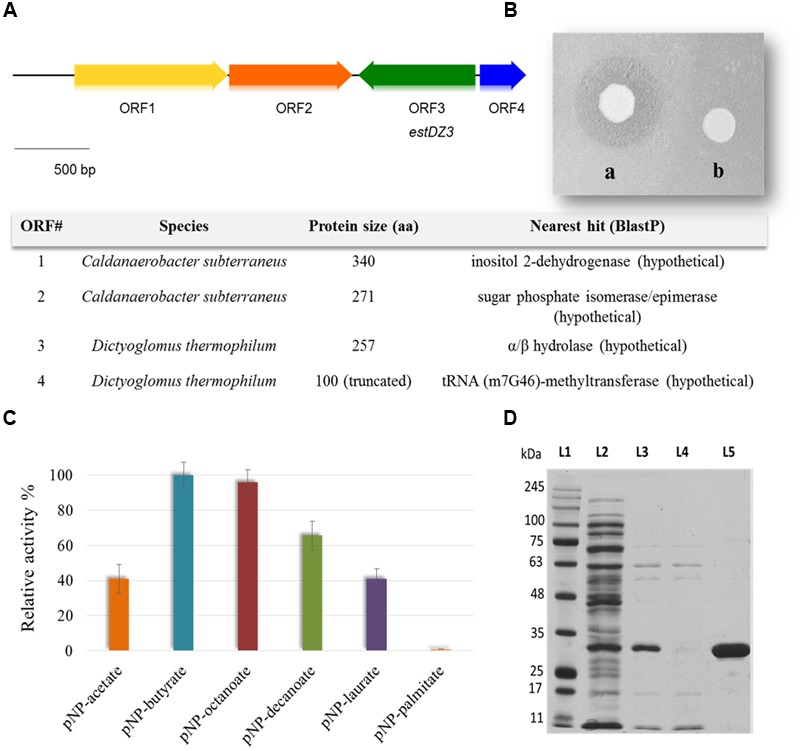
Discovery, identification and purification of EstDZ3. (A) Map of the 3.3 kb ch2 insert. ORFs indicated by arrows were annotated using BlastP and the closest homolog of each ORF is listed in the corresponding table (bottom). (B) E. coli BL21(DE3) cells carrying plasmid pLATE52-EstDZ3 (a) or empty vector (b), and grown on tributyrin-enriched agar containing 0.1 mM IPTG, the inducer of estDZ3 overexpression. (C) Initial substrate profiling of the esterolytic activity of EstDZ3 using clarified lysates of BL21(DE3) cells overexpressing estDZ3. Cell lysates were assayed against pNP esters of fatty acids with acyl chain lengths varying from C2 to C16. The relative enzymic activity was measured spectrophotometrically at 410 nm. The reported values correspond to the mean value from three independent experiments performed in triplicate and the error bars to one standard deviation from the mean value. (D) SDS-PAGE analysis of EstDZ3, after heat-treatment and IMAC purification. Protein bands were visualized by Coomassie staining. L1: molecular weight marker; L2: soluble lysate of E. coli cells producing EstDZ3; L3: soluble lysate of the same cells after heat treatment; L4: flow-through after loading of the IMAC column with the lysate corresponding to L3; L5: eluted EstDZ3 after imidazole addition. The predicted molecular weight of the recombinant enzyme is 31.6 kDa.
