Fig. 10.
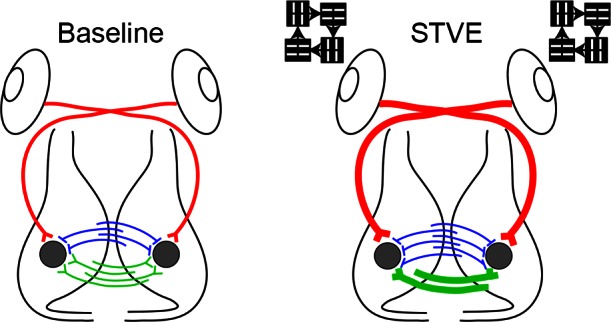
Summary diagram. Baseline: tectal neurons (gray circles) receive excitatory retinotectal (red), excitatory intertectal (green), and inhibitory intertectal (blue) inputs. STVE: with short-term visual enhancement (STVE), excitatory retinotectal input increases through addition of new synapses and strengthening of existing synapses. STVE increases both excitatory and inhibitory intertectal drive but via different mechanisms. STVE refines excitatory intertectal synapses by eliminating some boutons and by stabilizing and strengthening other synapses. In contrast, STVE increases inhibitory intertectal synapse number. The experience-dependent plasticity of intertectal inputs may help maintain the balance of excitation to inhibition in the optic tectum and keep tectal neurons functioning within a dynamic range in response to a changing visual environment.
