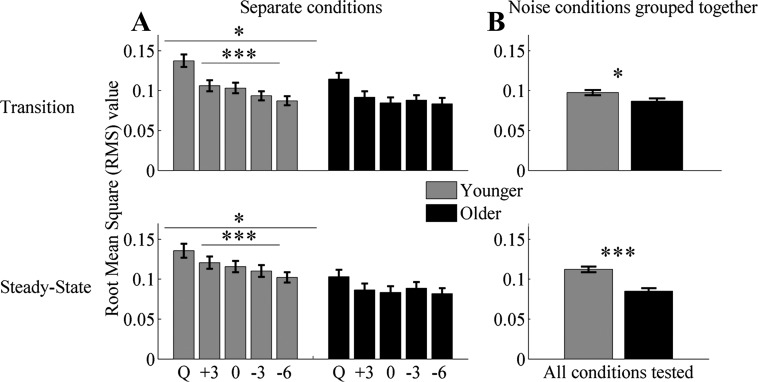
Fig. 3.
RMS values ± 1 SE of the envelope for the conditions (Q = Quiet, +3 = +3 dB, 0 = 0 dB, −3 = −3 dB, and −6 = −6 dB) tested in younger (gray bars) and older (black bars) adults. A: average RMS for each single condition. B: average RMS collapsed across all noise conditions tested. Younger adults had significantly higher RMS values in quiet in both the transition and the steady-state regions. An RMS × group-interaction effect was noted in the transition at −3 and −6 dB but not in the steady-state region. Repeated-measures ANOVA, applied to the 4 noise conditions, shows significant differences in younger adults in both the transition and steady-state regions but not in older adults. Noise minimally affects older adults, likely because their response in quiet is already degraded. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.